AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associates Certification
My notes for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associates Certification https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-solutions-architect-associate/?nc1=h_ls
Table of Contents
00 Plan of Attack
Important Resources
Learning
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect C02 - although outdated from (SAA-C03), core concepts are similar, SAA-C03 just has more stuff added to AWS
- Solutions Architect - Knowledge Badge Readiness Path 🔗
- Exam Prep Enhanced Course: AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate (SAA-C03) 🔗
- AWS Cloud Quest: Solutions Architect 🔗
Practicing
- https://www.udemy.com/course/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate-amazon-practice-exams-saa-c03/
- Exam Prep Official Practice Question Set: AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate (SAA-C03 - English) 🔗
- Exam Prep Standard Course: AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate (SAA-C03) 🔗
Domain 1: Design Secure Architectures (30% of scored content) Domain 2: Design Resilient Architectures (26% of scored content) Domain 3: Design High-Performing Architectures (24% of scored content) Domain 4: Design Cost-Optimized Architectures (20% of scored content)
01 Designing Secure Architectures
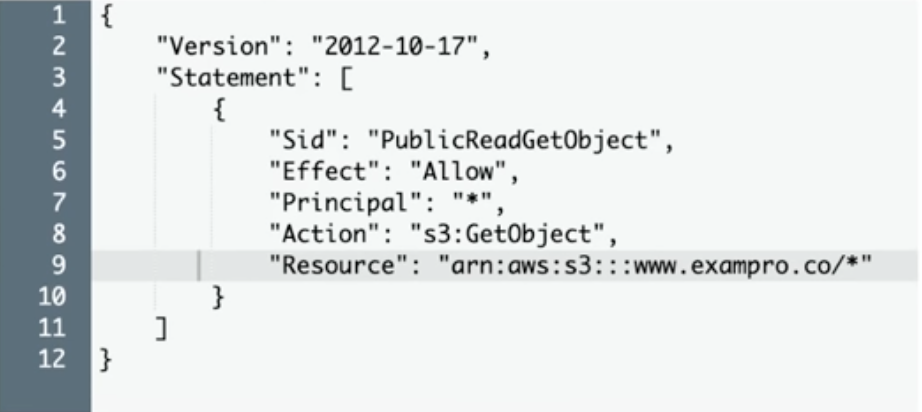
Simple Storage Service S3
 S3 Security
S3 Security
- Unique domain names!
- Buckets are PRIVATE by default.
- Access control is configured using Bucket Policies and Access Control Lists (ACL) although ACL is a legacy feature.
- Bucket Policies use a policy to define complex rule access.
S3 Encryption
- Encryption In Transit with Encryption in transit achieved via SSL/TLS
- Server Side Encryption (SSE)/Encryption At Rest with S3 Managed Keys (Amazon manages all the keys), SSE-AES, SSE-KMS and SSE-C
- Client-Side Encryption involves encrypting own files before uploading.
- Multi-Region KMS Key
S3 Data Consistency
-
New Objects (PUTS) - Read After Write Consistency
-
Overwrite (PUTS) or Delete Objects (DELETES) - Eventual Consistency
-
S3 Cross Region Replication (CCR) - when enabled, any objects that is uploaded will be automatically replicated to another regions. Versioning must be turned on for both the source and destination buckets.
-
S3 Versioning
-
S3 Lifecycle Management - automate the process of moving objects to different Storage classes or deleting objects all together. Can be used together with versioning. Can be applied to both current and previous versions.
-
S3 Transfer Acceleration - fast and secure transfer of files over long distance between your end users and an S3 bucket. Uses CloudFront’s distributed Edge Locations. Instead of uploading to your bucket, users use a distinct URL for an Edge Location. As data rrives at the Edge Location, it is automatically routed to S3 over a specialy optimized network path (AWS Backbone)
-
S3 Presigned Urls - An url generated via the AWS CLI and SDK. It provides temporary access to write or download object data. Presigned Urls are commonly used to access private objects.
-
MFA Delete - Users cannot delete objects from a bucket unless they provide their MFA.
- AWS CLI must be used to turn on MFA
- Bucket must have versioning turned on.
AWS Snowball - petabyte-scale data transfer service. Move data onto AWS via physical briefcase computer.
- Low cost - it cos thousands of dollars to transfer 100TB over high speed internet. Snowball can reduce that cost by 1/5th.
- Speed - it can take 100 TB over 100 days to transfer over high speed internet, it can reduce that ransfer time by less than a week.
- Features
- E-ink display
- tamper and weather proof
- encrypted end to end
- uses Trusted Platform Modules (TPM)
- data transfers must be completed within 90 days of the Snowball being prepared.
- Snowball can import and export from S3
- Size
- 50 TB (42 TB of usable space)
- 80 TB (72 TB of usable space) AWS Snowball Edge - similar to snowball but with more storage and with local processing
- features
- LCD display
- edge computing workloads
- cluster in groups of 5 to 10 devices
- storage optimized, compute optimized, GPU optimized
- Size
- 100 TB(83TB of usable space)
- 100 TB Clustered (45 TB per node) Snowmobile - a 45 foot long ruggedized shipping container, pulled by a semi-trailer truck, transfer up to 100PB per snowmobile.
- help you connect your network to the snowmobile and when the transfer is complete they’ll dirive it back to AWS to import into S3 or Glacier.
- Features
- GPS tracking
- alarm monitoring
- 24/7 video surveilance
- an escort secrutiy vehcile in transit (optional)
Virtual Private Cloud - provision a logically isolated section ofthe AWS cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define.
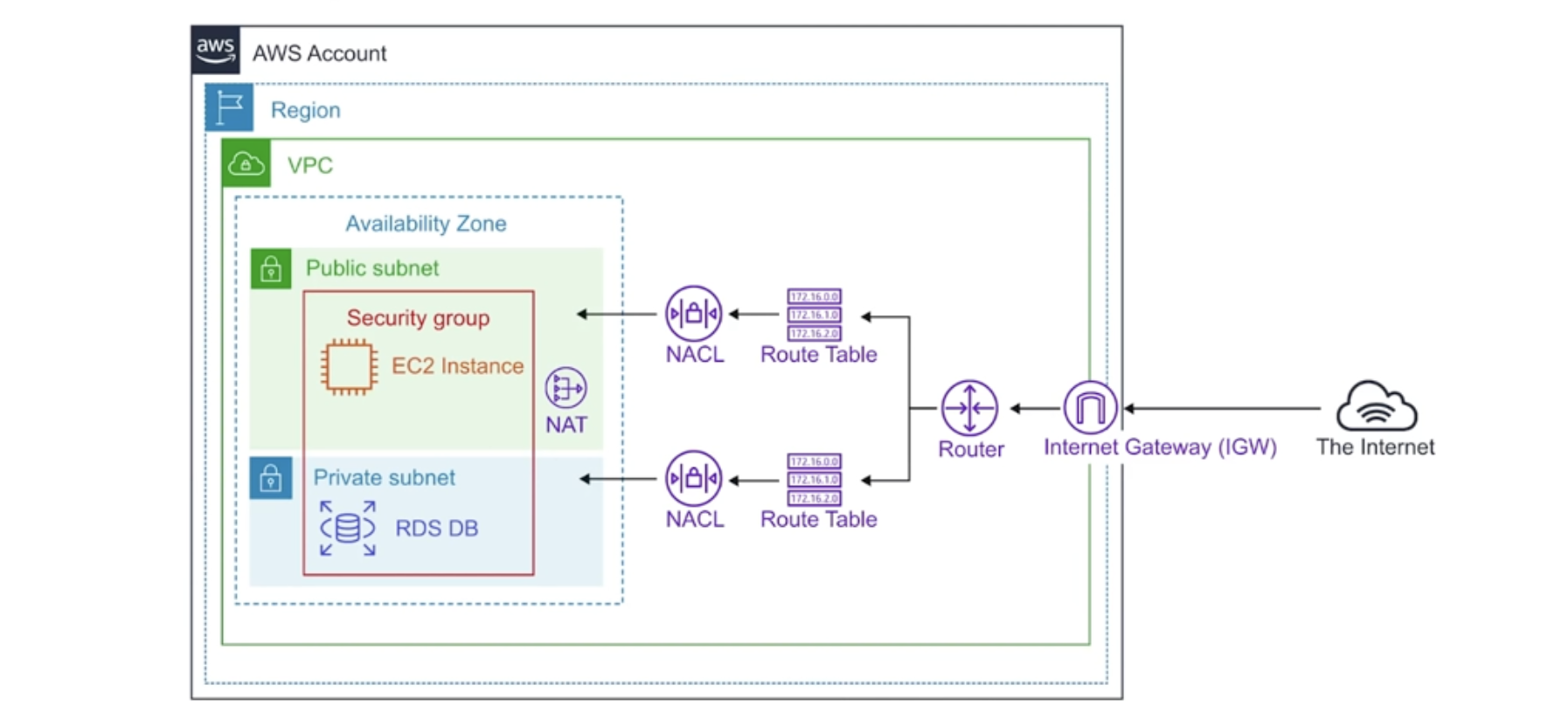 Features
Features
- Can span AZs?
- VPCs are region specific
- Can create up to 5 VPC per region
- Every region comes with a default VPC
- Can have 200 subnets per VPC Can use the IPv4 CIDR Block in addiition to a IPv6 CIDR Blocks (the address of the VPC)
- Free: VPC’s, Route Tables, NACLs, Internet Gteways, Security Groups, and Subnets, VPC Peering
- Paid: NAT Gateway, VPC Endpoints, VPN Gateway
- DNS hostname (should your instance have domain name address)
AWS has a default VPC in every region so you can immediately deploy istances
- VPC with a size /16 IPv4 CIDR block (172.31.0.0/16)
- Size /20 default subnet in each AZ
- Connect an Internet Gateway
- Default security group
- Default NACL
- Default DHCP
- Automatically has main route table.
VPC Peering allows you to connect one VPC with another over a direct network using private IP address.
- No Transitive Peering
- No Overlapping CIDR Blocks
- Uses Star Configuration
Route Tables are used to determine where network traffic is directed. Each subnet in your VPC must be associated with a route table. A subnet can only be associated with one route table at a time, but you can associate multiple subnets with the same route table.
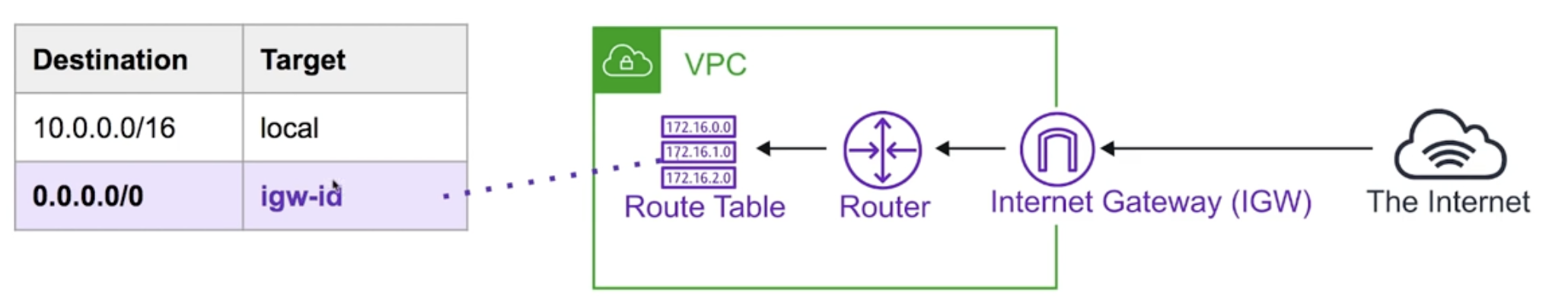
Internet Gateway allows access your VPC access to internet.
- It provides a target in your VPC route table for internet-routable traffic.
- Perform NAT for instances that have been assigned public IPv4 address.
Bastion/Jumpbox are designed to help gain access to EC2 instances via SSH or RCP that are ina private subnet.
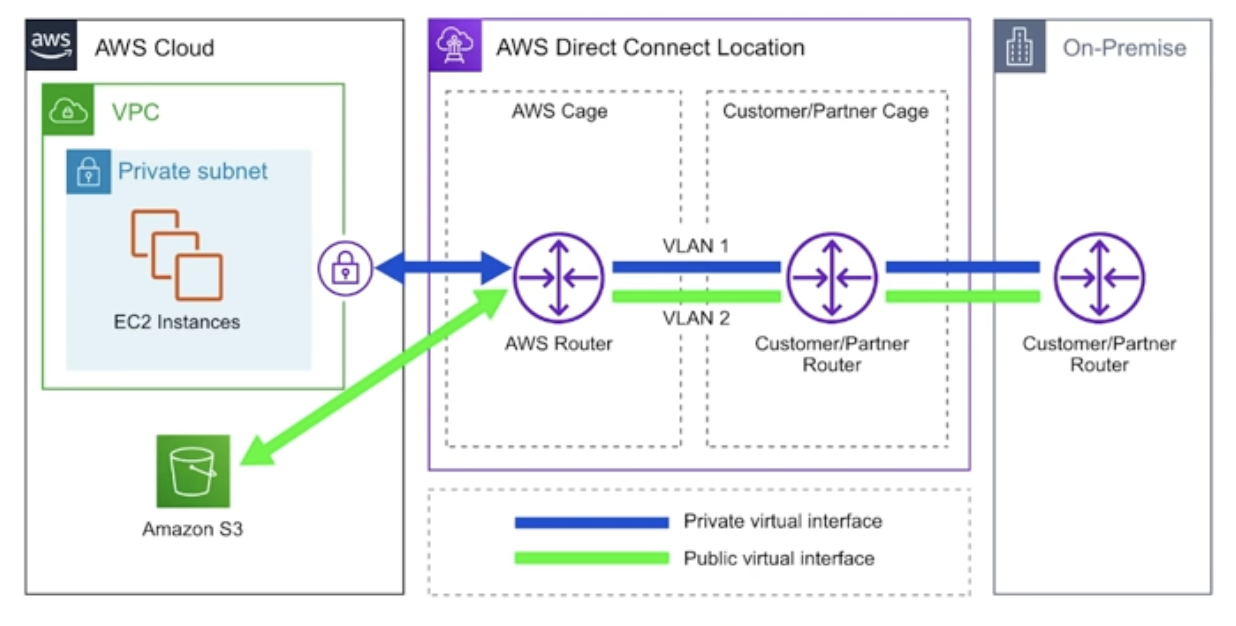
AWS Direct Connect is AWS solution for establishing dedicated network connectsions from on-premisis locations to AWS.
- Very fast. Lower bandwidth 50-500M, higher bandwidth 1GB or 10GB.
- Helps reduce network costs and increase bandwidth throughput.
- Provides a more consistent network experience.
VPC Endpoints allow you to privately connect your VPC to other AWS services, and VPC endpoint services. Keep traffic within the AWS network!
- Eliminates the need for IG, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect
- Instances in the VPC do not require public IP.
- Interface Endpoints - Elastic Network Interface (ENI) with private IP address. They serve as an entry point for traffic going to a supported service. Supports a ton of interfaces.
- Gateway Endpoints - Gateway endpoing is a gateway that is a target for a specific route in your route table, used for traffic destined for a supported AWS service. Only supports DynamoDB and S3, but is free.
VPC Flow Logs allow you to capture IP traffic information in and out of Network Interfaces within your VPC. Can be created for VPC, Subnets, and Network Interface, stored in VPC CloudWatch.
- cannot be tagged
- cannot change the config after it’s created
- cannot enable flow logs for VPCs which are peered with your VPC
- contain source and destination IP address (not hostnames)
- not monitored
NACLs - optional layer of security that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of subnet(s)
- Unlike security groups, can allow or deny inbound and outbound
- NACL defy all traffic by default
- subnets are associated with NACLs, subnets can only belong to a single NACL.
- Stateless
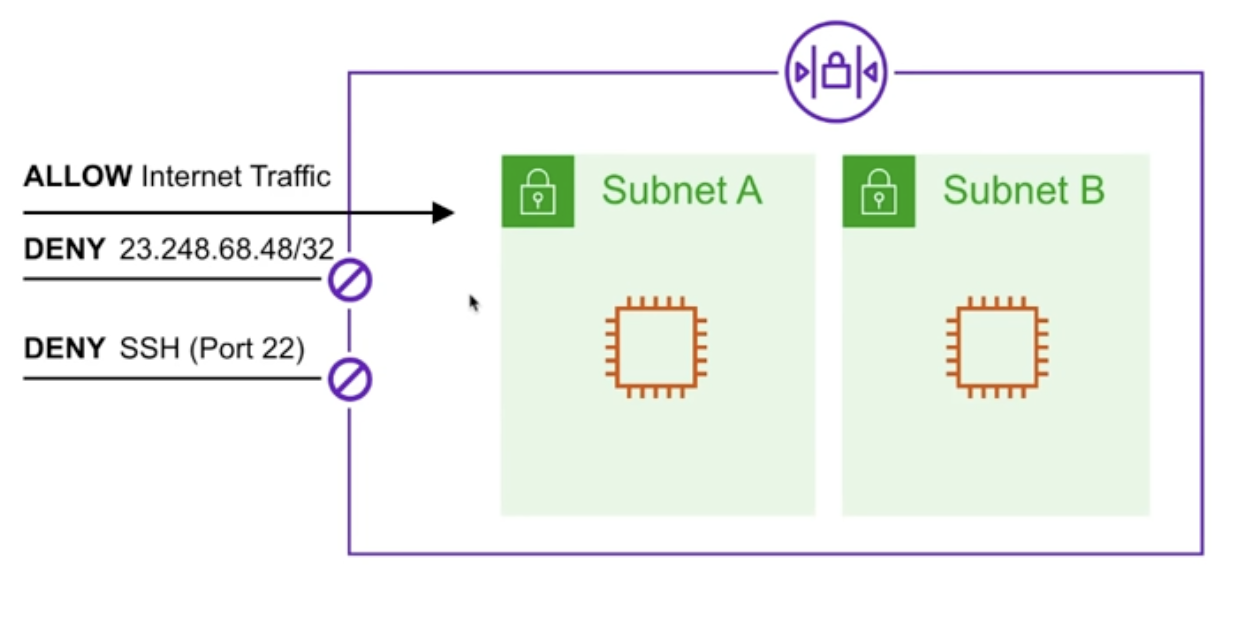
Security Groups - a virtual firewall that control that control the traffic to and from EC2 instances.
- multiple instances across multiple subnets can be long to a security gro[.
- no deny rules, all traffic is blocked by default unless a rule specifically allows it.

- Limits - up to 10,000 security groups in a region (default is 2,500), 60 inbound rules and 60 outbound rules per security group, 16 security groups per elastic network interface (ENI), default is 5
- stateful
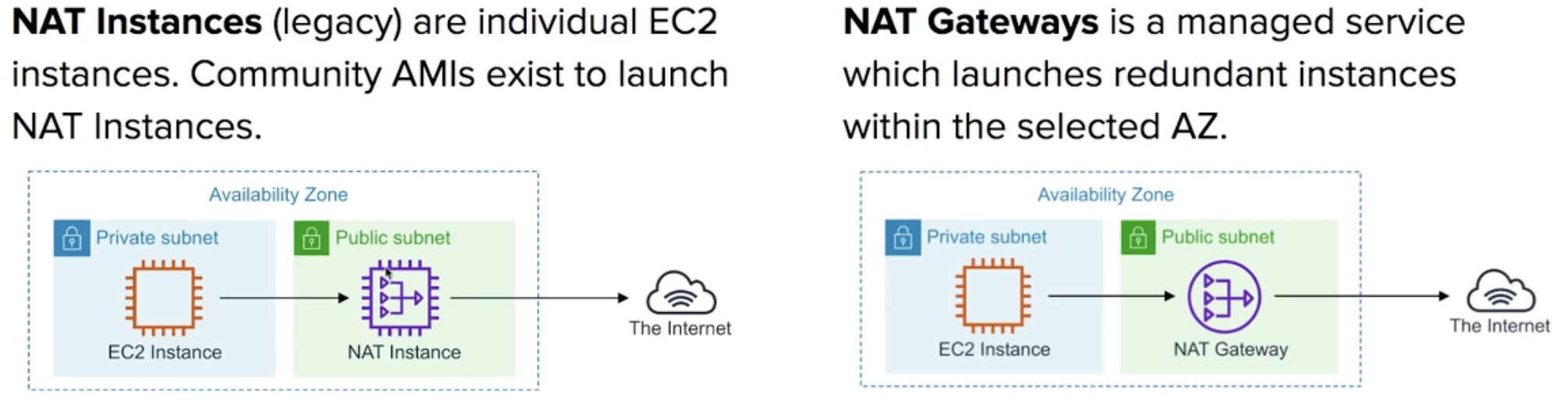
Network Address Translation (NAT) is the method of re-mapping one IP address space into another.
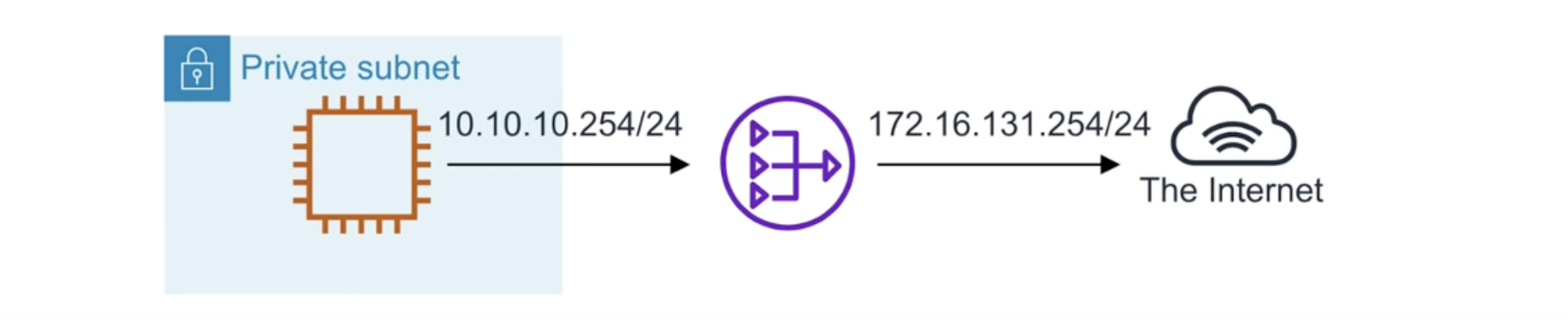
- NAT Instances
- must disable source and destination checks on instance
- size of NAT instances determines how much traffic can be handled
- high availability can be achieved using autoscaling groups
- NAT Gateways
- redundant inside an Availability Zone (can survive failure of EC2 instances)
- 1 NAT Gateway inside 1 AZ (cannot span AZs)
- preferred for enterprise systems
- 5Gbps to 45 Gbps
- no requirement to patch NAT gateways, no need to disable source/destination checks
- automatically assigned a public IP address
- Route Tables must be updated
- Resources in multiple AZs sharing gateway will lose internet access if gateway goes down, unless you create a gteway in each AZ and configure route tables accordingly
IAM - IAM allows management of access of users and resources. IAM identities include users, groups, and roles. IAM Policies are JSON documents which grant permissions for a specific user, group, or role to access services. You associate permissions (policies) to a role and assign it to users or groups.
- user can belong to a group, roles can be applied to groups to quickly add and remove permissions en-masse to users.
- an user can have a role directly attached an policy can be directly attached to a user (called inline policy)
- is a uiversal system (applied to all regions in the same time)
- free service
- new IAM accounts have no permisisons by default
Managed Policies - policy which is managed by AWS, which you cannot edit. Managed policies are labeled with an orange box.
Customer Managed Policies - Policy created by the customer which is editable. Customer policies have no symbol beside them.
Inline Policy - policies that are directly attached to the user
Policy Structure -

Password Policy - to set the minimum requirements of a password and rotate passworods.
Access Keys - allow users to interact with AWS service programmatically via the AWS CLI or AWS SDK. Allowed two access keys per user.
- only showed once when created, must be deleted/recreated account
MFA - multi-factor authentication can be turne on per user. user has to turn on MFA themselves, administrator cannot directly enforce. THe administrator account could create a policy requirng MFA to access certain resources.
- Always set up MFA for root aaccounts
Cognito - decentralized managed authentication, sign up, sign in integration for your apps. Social identity provider such as Facebook and google.
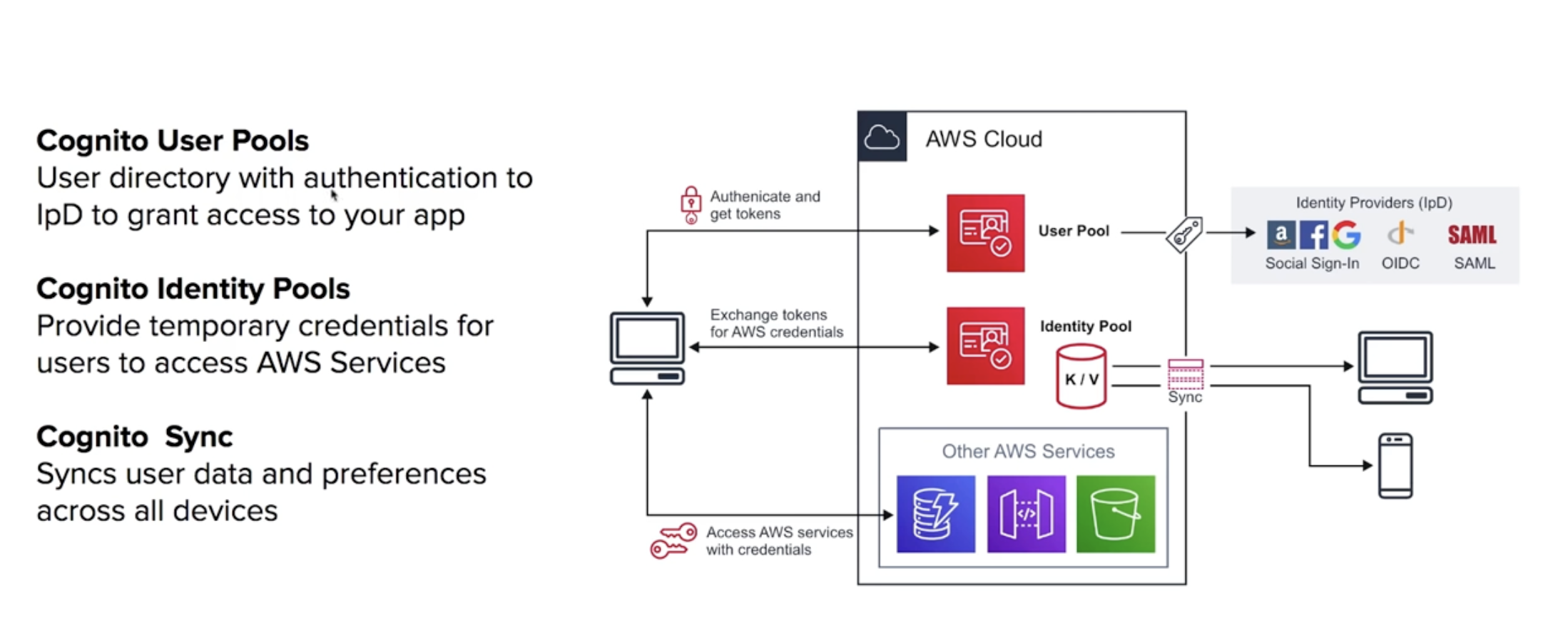
Web Identity Federation - to exchange identity and security informtation between an identity provider (IdP) and an application.
IdP - a trusted provider of your user identity that lets you use authenticate to access other services. Includes FB, Amazon, Google, LinkedIn, etc. Technologies include Single Sign On (SSO) - SAML - OpenID Connect (OIDC) OAuth (for Web Identity Federation)
User Pools - user directors that are used to manage actions for web and mobile apps such as
- sign up
- sign in
- account recovery
- account confirmation
Identity Pools - provide temporary AWS credentials to access services.
Cognito Sync - sync user data and preferences across devices with one line of code. Uses push synchorniation to push updates and synchronize data. Use SNS.
Command Line Interface - les you interact with AWS from anywhere by simply using a command line.
Software Development Kit - set of API libraries that let you integrate AWS services into your applications. he SDK is available for the following languages.
Progrmatic Access Access Key and Secret - when you enable progmattic access for AWS users. You have the ability to create Access Key ID and Secret Access Key. These are collectively known as AWS Credentials.
- Must be enabled per user via the IAM console
- CLI is installed via a Python script.
Domain Name System - the phonebook of the internet, DNS translates domain names to IP address so browsers can find internet resources.
- gets registered through InterNIC, service provided by ICANN and enforces the uniqueness of domain names all over the internet.
- top level domain are controlled by ,IANA
- every domain must have an Start of Authority (SOA), which is a way for the domain admins to provide information about the domain, every zone can only have one SOA.
- Address Records convert the name of domain directly to an IP address
- Canonical Names resolve one domain to another domain, rather than an IP address.
- Name Server Records (NS) are used by top level domain servers to direct traffic to the DNS server containing the authoritative DNS records.
- TTL - length of time that a DNS record gets cached (lowe time means changes propagate faster)
Route 53 is a Domain Name Service, more snergies with AWS Services
- register and manage domains
- create various records set on a domain
- implement complex traffic flows
- continously monitor records via health checks
- resoluve VPC’s outside AWS
- heatlh checks
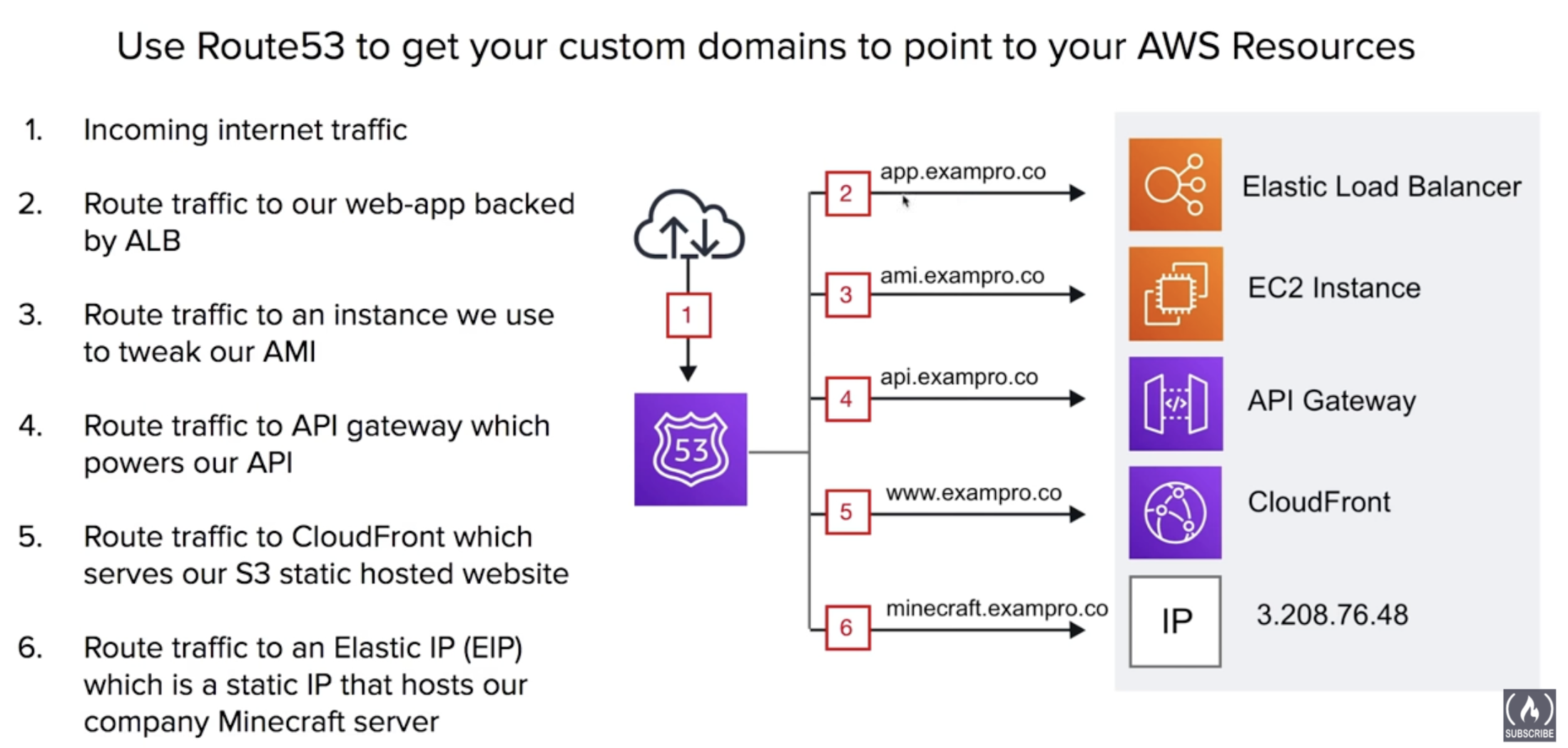
Record Sets - create record sets which allows us to point our naked domain and subdomains via Domain records. For example, we can send our WWW subdomain using an A record to point a specific IP address.
Traffic Flow - a visual editor that allows you to create sophisticated routing configurations for resources using existing routing types.
Simple Routing Policies are the most basic routing policies in Route53 Defaut Policy
- you have 1 record and provide multiple IP address
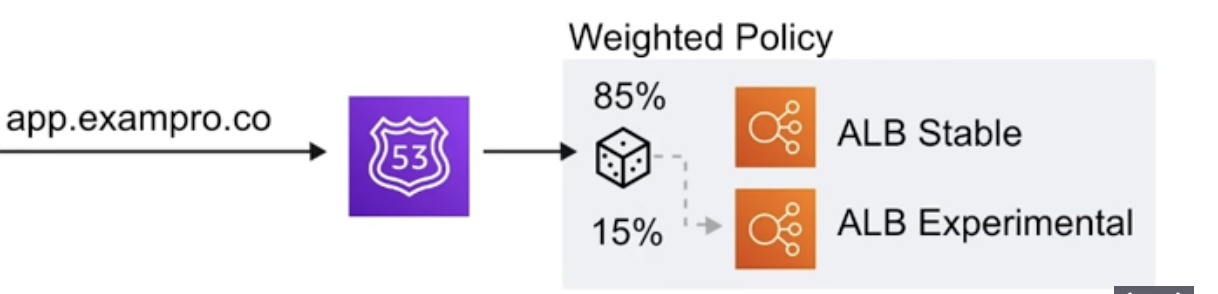
- when multiple values are specified for a record, Route 53 will return all values back to the user in a random order. Weighted Routing Policies
- good for ALB testing
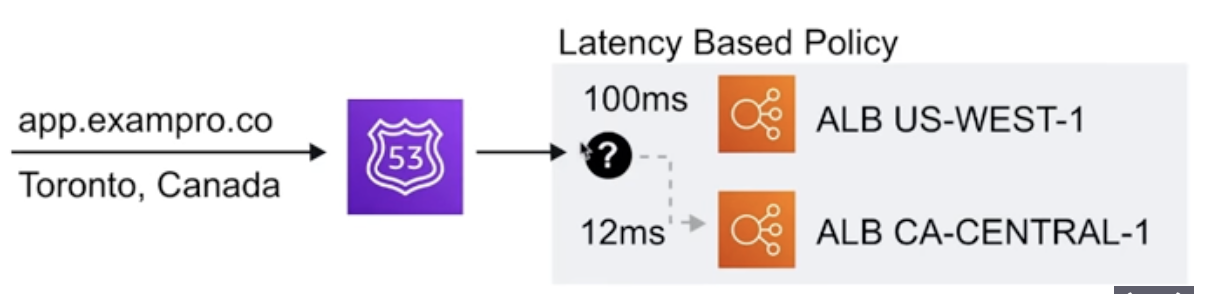
 Latency Based Routing Policies — allows you to direct trafic based on the lowest network latency possible for your end-user based on region.
Latency Based Routing Policies — allows you to direct trafic based on the lowest network latency possible for your end-user based on region. - Requires a latency resource record to be set for EC2 or ELB resource that hosts your application in each region.
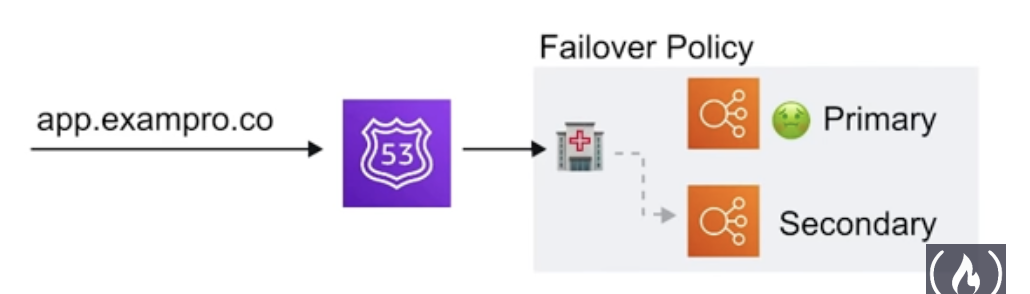
Failover Routing Policies - allow you to create active/passive setups in situations where you want a primary site in one location and a secondary data recovery site in another
 Geolocation Routing Policies - allow you to direct traffic based on the geographic location of where the request originated from.
Geoproximity Routing Policies - allow you to direct traffic based on the geographic location of your users and AWS resources
Geolocation Routing Policies - allow you to direct traffic based on the geographic location of where the request originated from.
Geoproximity Routing Policies - allow you to direct traffic based on the geographic location of your users and AWS resources
- Must use Route 53 Traffic Flow in order to use geoproximity routing policies
- Multi-Value Answer Policy - same as simple but with health checks! Routes to healthy one after random choice.
Route53 Resolver - regional service that lets you route DNS queries betweeen your VPC and Network, for hybrids.
EC2 - highly configurable service, resizable compute compacity, takes minutes to launch new instances. anything and everything on AWS uses EC2 instance underneath
- EC2 instances sizes generally double in price and key attributes
Instance Types and Usages

Instance Profile - instad of embedding your AWS credentials (access key and sceret) in your code, instead attach a role to an instances via Instance Profile.
Placement Groups - let you choose the logical placement of your instances to optimize for communication, performance, or durability. Placement groups are free.
- Cluster
- packs instances close together in an AZZ
- low latency network performance
- well suited for HPC applications
- clusters cannot be multi-AZ
- Partition
- ispread instances across logical partitions
- each partition do not share the underlying hardware with each other (rack per partition)
- well suite for large distributed and replicated workloads (Hadoop, Cassandra, Kafka)
- Spread
- each instance is placed on a different rack
- when critical instances should be kept separate from each other
- can spread a max of 7 instances. Spreads can be multi-AZ
UserData is a script that will be automatically run when launching an EC2 instance, you could install package, apply updates or anything you would like.
MetaData - from within your instance you can access information about the EC2 via a special url endpoint.at http://169.254169.254/latest/meta- data
Pricing Model
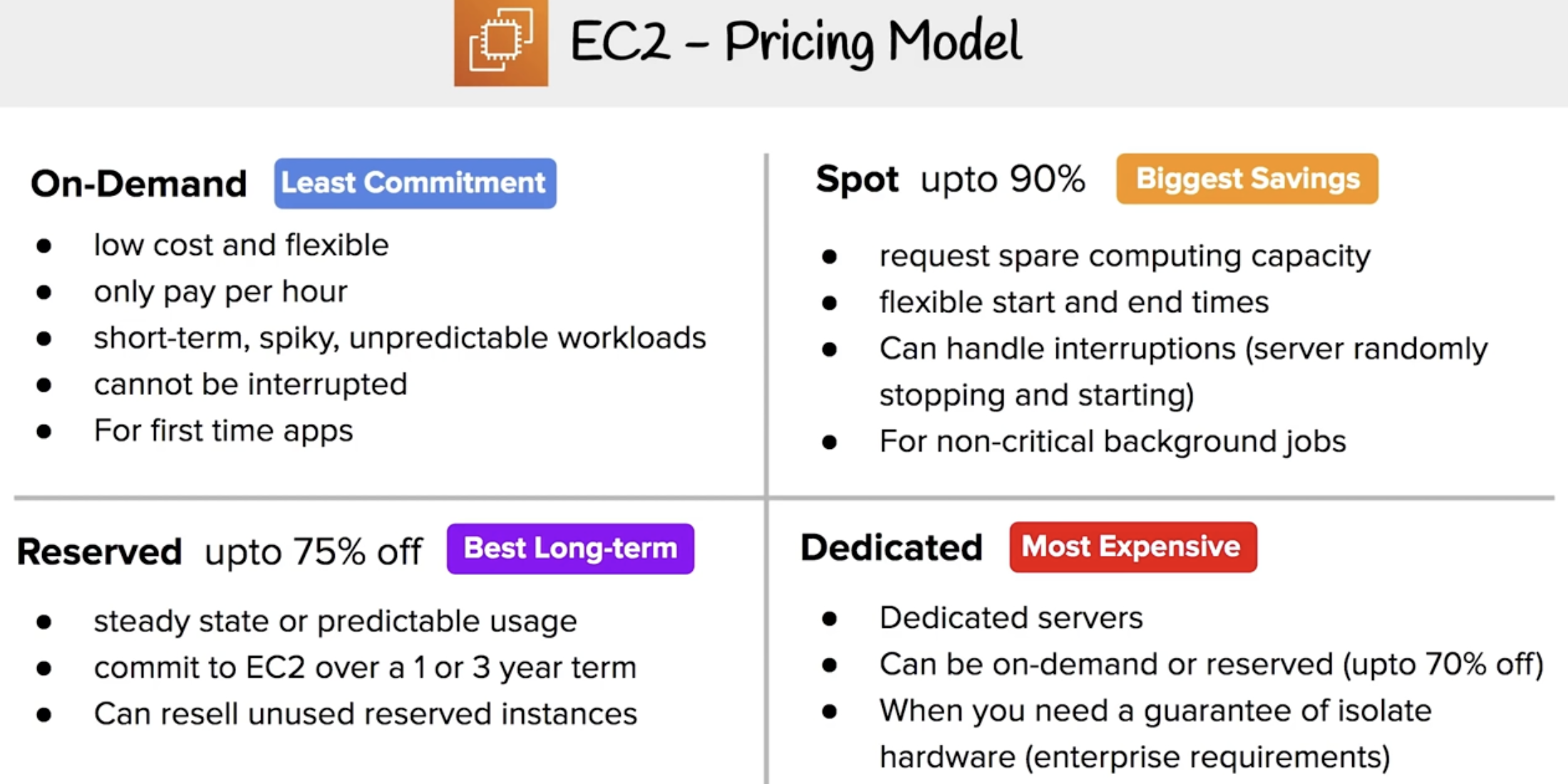 Resrved
Resrved
- Standard up to 75%
- Convertible up to 54%
- Scheduled reserved instances for specific time periods
RI’s can be shared between multiple accounts within an ORG. Unused RIs can be sold in Reserved Instance Marketplace
Spot Instances - designed for applications that have flexible start and end times or applications that are only feasible at very low compute costs.
- Good for AWS Batch
Amazon Machine Instance - a template to configure new instances - can turn EC2 instances into AMIs so you can create copies of your servers.
- AMIs help you keep incremental changes to your OS, application code, and system packages.
- A template for the root volume for the instance (EBS Snapshot or Instance Store template)
- Launch permissions that control which AWS accounts can ue the AMI to launch instances.
- Region Specific, can copy to another region using the Copy AMI command.
- Community AMI are free AMIs maintained by the community
- AWS Marketplace free or paid subscription AMIs maintained by vendors
- AMIs have an AMI ID, the same AMI eg will vary in both AMI ID and options. Architecture options in different regions.
EC2 Auto Scaling Groups set scaling rules which will automatically launch additional EC2 instance or shutdown instances to meet current demand.
- COntains a collection of EC2 instances that are treated as a group for the purpose of automatic scaling management.
- Can occur via Capacity Settings, Health Check Replacements, Scaling Policies
- Target Scaling Policy - Maintains a specific metric at a target value.
- Simple Scaling Policy - Not recommended now…
- Scaling Policies with Steps - Scales when an alarm is breached, can escalate based on alarm value changing.
- Can be associated with Elastic Load Balancers (ELB)
- Launch Configuration - a launch configuration is an instance configuration template that an Auto Scaling group uses to launch EC2 instances, can not be edited.
- Launch Templates - are Launch Configurations with Versioning.
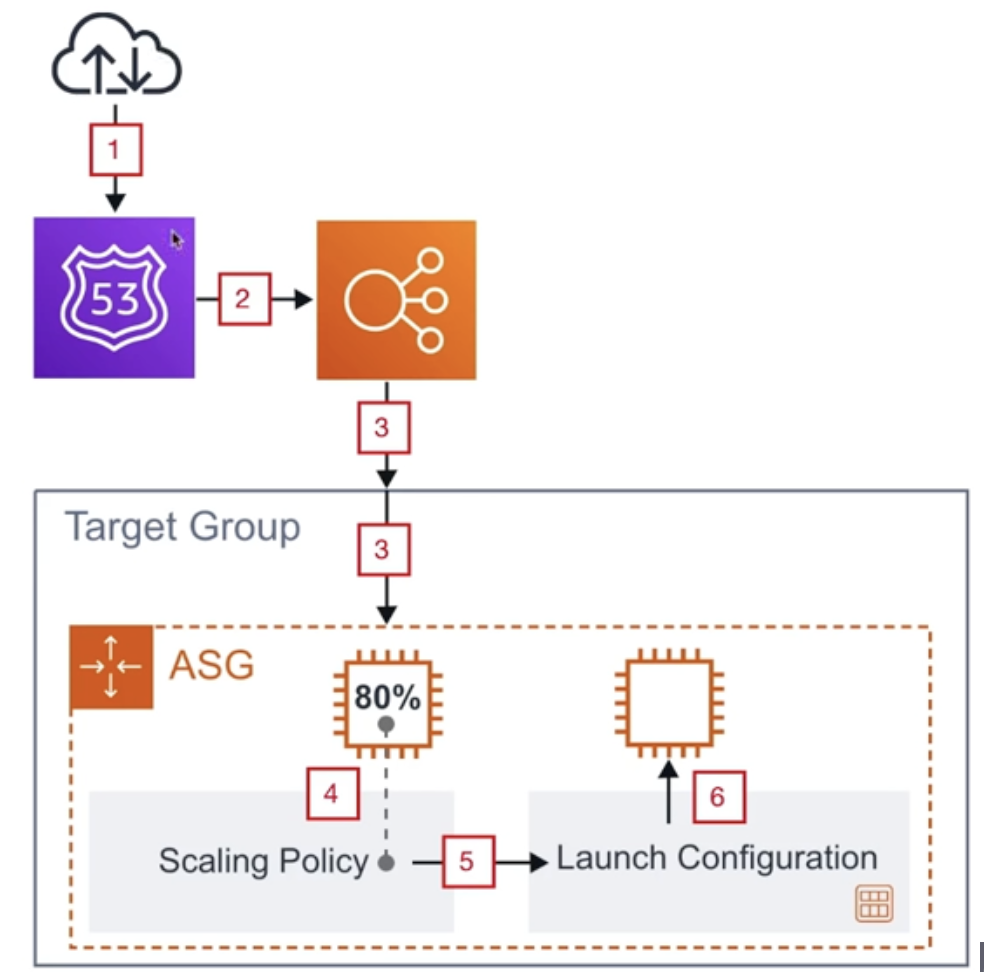
Elastic Load Balancers - distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets.
- Application Load Balancer - designed to balance HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Operate at Layer 7 of the OSI Models. HAs a feature called Request Routing. WAF can be attached to ALB.
- Network Load Balancer - designed to balance TCP/UDP, operate at layer 4 of OSI Model, good for high throughput such as Video Games
- Classic Load Balancer - legacy
- Gateway Load Balancer - designed for inspection…
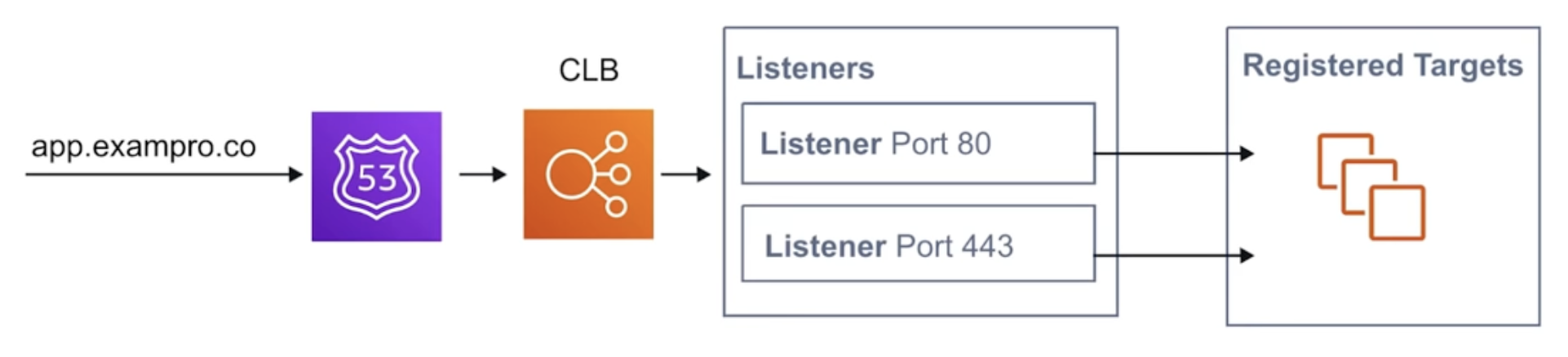 Can attach Amazon Certificate Manager SSL to any of the ELB’s.
Can attach Amazon Certificate Manager SSL to any of the ELB’s.
The Rules of Traffic
- Listeners - incoming traffic is evaluated against listeners. Listeners evaluate any traffic that matches the Listener’s port. For CLB, EC2 instances are directly registered to the Load Balancer.
- Rules - (Not available for CLB), listeners will then invoke rules to decide what to do with the traffic. Generally the next step is to forward traffic to a target group.
- Target Groups (Not available for CLB)\
Sticky Sessions - advanced load balancing method that allows you to bind a user’s session to a specific EC2 instance. Ensures all requests from that session are sent to the same instance.
- Typically utilized with Classic Load Balancer.
- Can be enabled for ALB though can only be set on a target group not individual EC2 instances.
- Cookies are used to remember.
X-Forwarded-For Header
ELB Health Checks - Instances are monitored by ELB report back Health Checks as InService or OutofService.
- Does not terminate unhealthy instances, just redirect traffic to healthy instances.
Cross-Zone Load Balancing - Only for classic and network load balancer.
- Enabled - requests are distributed across evenly across instances in all enabled AZ
- Disabled - requests are distributed evenly across the instances in only its AZ
ALB - Request Routing - apply rules to incoming request and then forward and redirect traffic.
Elastic File System - cloud native NFS file system - attach a single file system to multiple EC2 instances, don’t worry about running out or managing disk space.
- capacity grows (up to petabytes) and shrinks automatically based on data stored (Elastic)
- using the Network FIle System version 4 (NFSv4)
- data is stored across multiple AZs
- Read after write consistency
- Create mount point
- Can support thousands of concurrent connections over NFS.
Elastic Block Store - virtual hard drive in the cloud, create new volumes, attach to EC2 instances, backup via snapshots and easy encryption.
- IOPS stand for Input/Output per second. It is the speed at which non-contiguous reads and writes can be performed on a storage medium. High I/O = lots of small fast reads and writes.
- Thoroughput - the data transfer rate to and from the storage medium in megabytes per second.
- Bandwith - the measurement of the total possible speed of data movement along the network.
- highly durable for attaching persistent block storage, volumes are automatically replicated within their AZ to protect from component failure.
- have termination protection (don’t delete on termination protection)
- There is something called Fast Snapshot!
5 Types of EBS Storage
- General Purpose (SSD)
- Provisioned IOPS (SSD)
- Troughput Optimized HDD
- Cold HDD
- EBS Magnetic
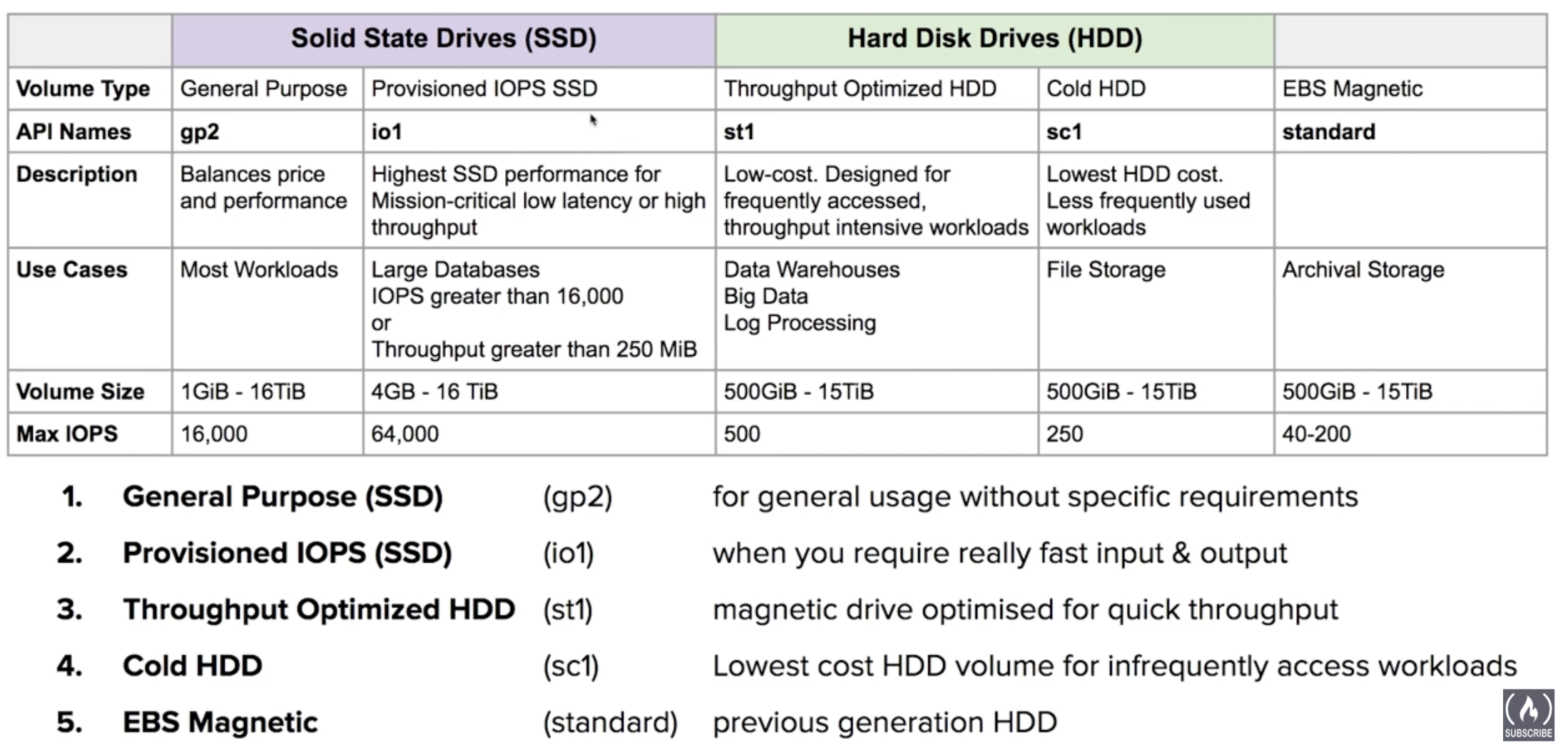
HDD - good at writing a continuously amount of data
- not good for writing many small reads and write
Medium SDD - very good at frequentyl reads and writes, uses integrated circuits, quicer access time and lower latency
Magnetic Tape - Durable for decades, cheap.
Moving Volumes - From one AZ to another
- take a Snapshot of the volume
- create an AMI from the snapshot
- launch new EC@ instance in dezired AZ
From one Region to Another
- Take a Snapshot of the volume
- Create an AMI from the Snapshot
- Copy the AMI to another region
- Launch a new EC2 instance from the copied AMI
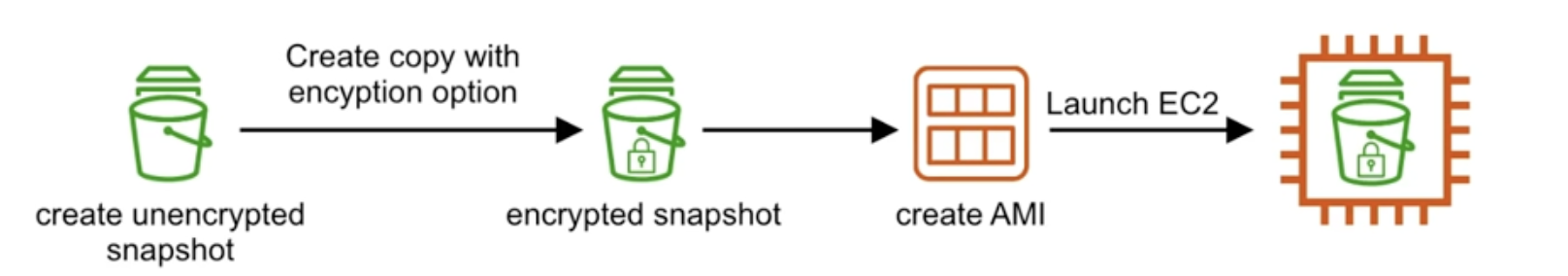
Encrypted Root Volume
- Take a snapshot of the unencrypted volume
- create a copy of that snapshot and select encryption option
- create a new AMI from the encrypted Snapshot
- Launch a new EC2 instance from the Created AMI
Snapshots or restored encrypted volumes will ablso be encrypted You cannot share a snapshot if it has been encrypted Unencrypted snapshots can be shared with other AWS accounts or made public.
 EBS vs Instance Store Volumes
An EC2 instance can be backed (root device) by an EBS Volume or Instance Store.
EBS vs Instance Store Volumes
An EC2 instance can be backed (root device) by an EBS Volume or Instance Store.

CloudFront - CDN, cache copies in Edge loctions.
- Can be used to deliver an entire website, including static, dynamic, and streaming.
- Requests for content are served from the nearest Edge Location for the best possible.
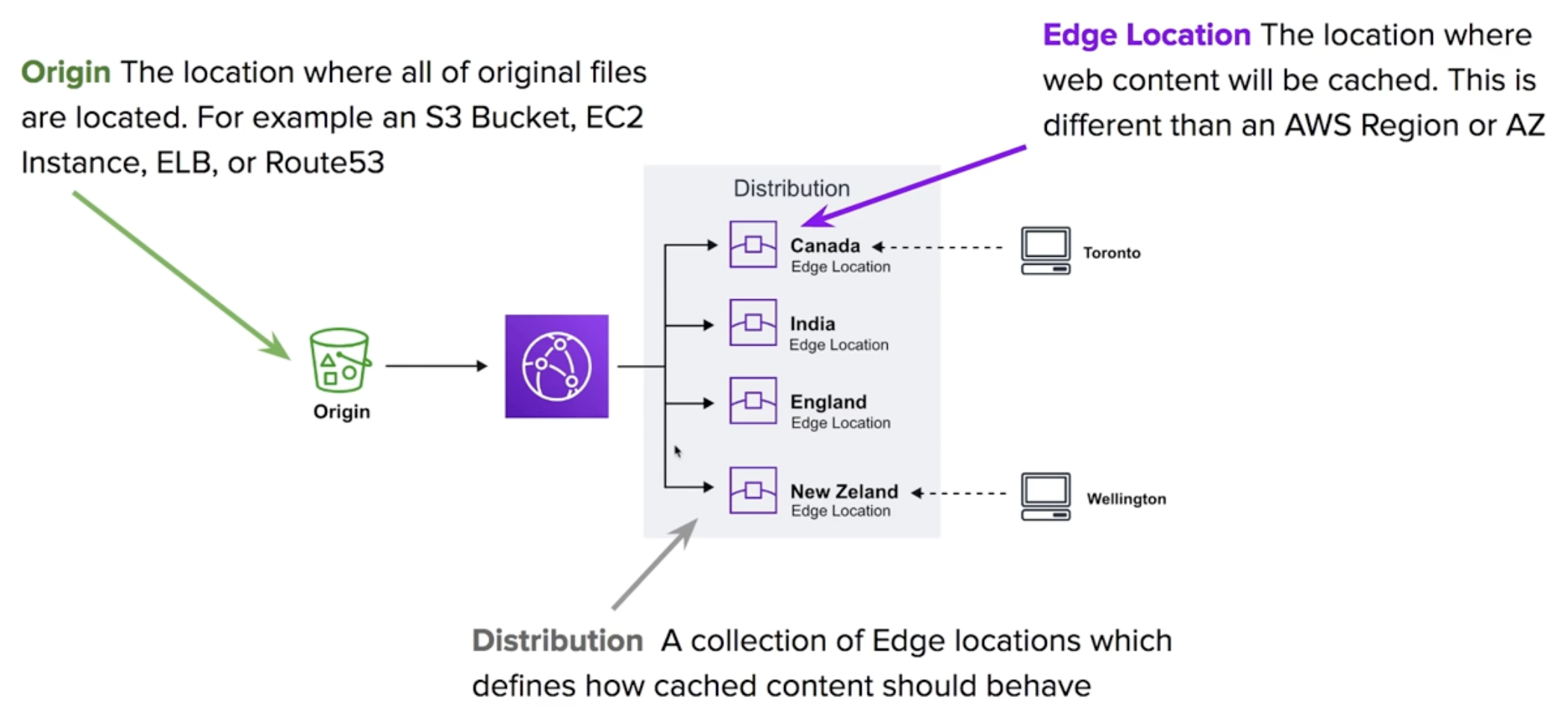
CloudFront - Distributions - a collection of Edge Locations.
- you specify the origin
- replicates copies based on price class
- two types of distributions, Web, and RTMP (for streaming media)
- behaviors
- invalidations
- error pages
- restrictions
- TTL - defines how long until the cache expires (referesh caches) ← cost money
Lambda@Edge are functions that override the behavior of request and responses.
- Viewer request
- Origin request
- Origin response
- Viewer response
CloudFront - Protection
- Original Identity Access (OAI) - virtual user identity that will be used to give Cloud front Distribution permission to fetch a private object - used to access private S3 buckets.
- Signed URLS - a url with provides temporary access to cached objects (NOT THE SAME AS S3 presigned URL)
- Signed Cookies - a cookie which is passed along with the request to CloudFront. The advantage of using a Cookie is you want to provide access to multiple restricted files.
- Access to cached content can be protected by signed urls or signed cookies.
Relational Database Service (RDS) A managed relational database service.
- Currently has 6 relational database - Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, Postgres, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server
- managed by AWS, cannot SSH into the VM running the database
RDS Encryption
- turn on encryption at rest for all RDS engines (maybe except for some older version)
- will also encrypt automated backups, snapshots, and read replicas.
- encryption is handled using AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
RDS Backups
- automated backups, choose retention period between 1 and 35 days
- no additional charge for backup storage
- storage I/O may be suspended during backup
Manual Snapshots
- taken manually by the user
- backups persist even if you delete the original RDS instance
RDS Restoring Backup
- when recovering, AWS wiill take the most recent daily backup, and apply transaction log data relevant to taht time, this allows point-in-time recovery data to a second inside the retention period
- backup data is never restored overtop an existing instance
- when you restore an RDS instance from automated backup or a manually snapshot, a new instance is created for that restored database
- restored RDS instances will have a new DNS endpoint.
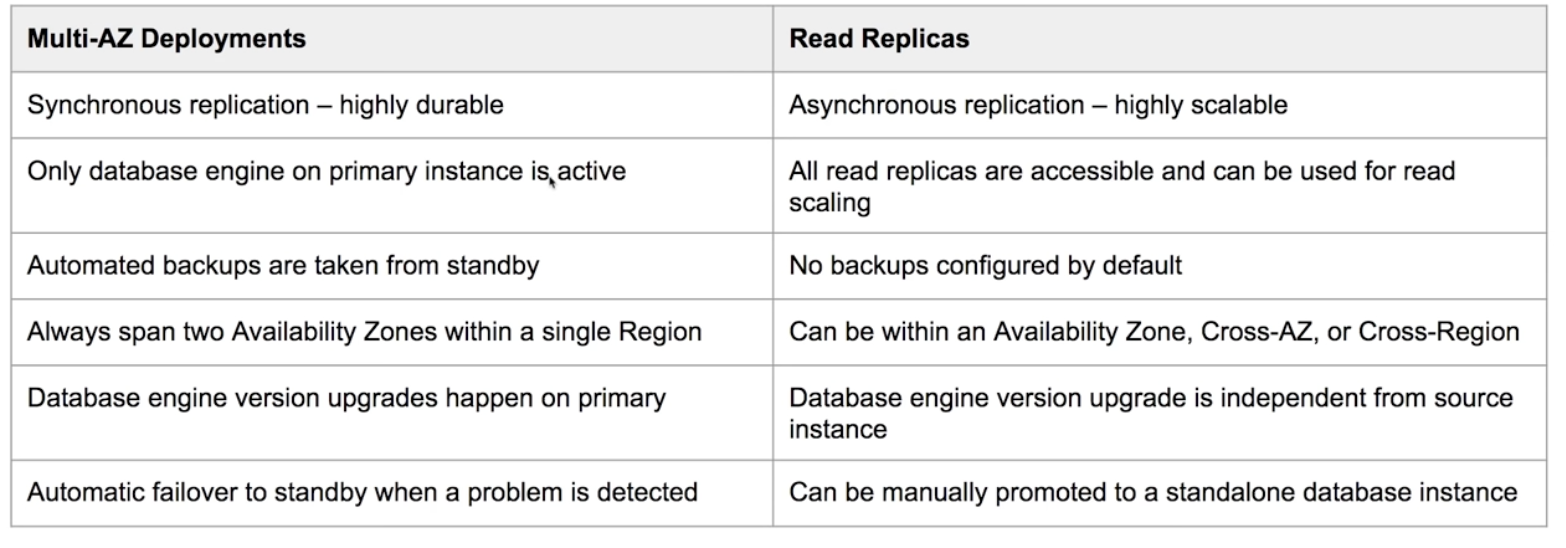
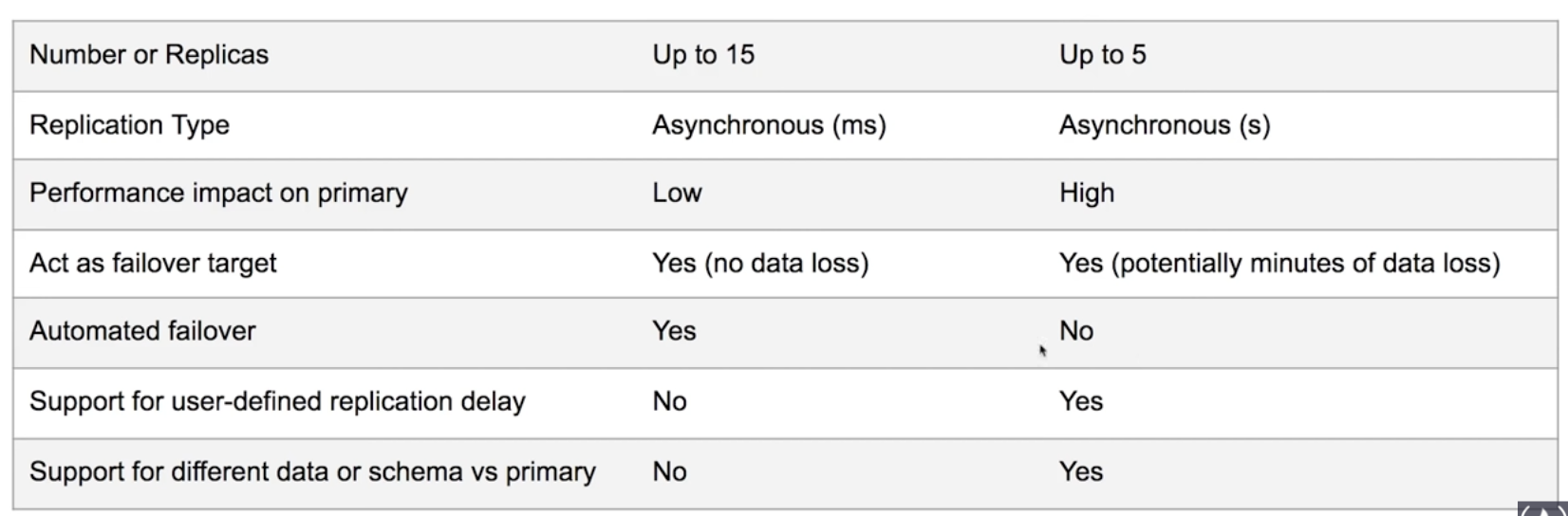
RDS - Multi- AZ - ensures database remains available if another AZ becomes unavailable, has uatomatica failover protection RDS - Read Replicas - asynchronous replication between primary RDS instance and the replicas.
- you can have up to 5 replicas of a database
- each read replica will have its own DNS Endpoint
- you can have Multi-AZ replicas, replicas in another region, or even replicas of other read replicas.
- replicas can be promoted to their own database, but this breaks replications.
- no automatic failover.
- Cross-Region Replicas
Aurora - fully managed postgres or MySQL compatible database designed by default to scal and fine-tuned to be really fast.
-
combines the speed and availability of high-end databases
-
with the simplicty and cost-effectiveness of open source databases
-
5x the performance than traditional MySQL
-
3x the performance than traditional Postgress
-
1/10 the cost
-
allowed up to 15 Aurora Replicas
-
Database can span multiple regions via Aurora Global Database
-
Scaling - Star up with 10GB of storage, and scale in 10GB increments up to 64 TB, autoscaling, computing resources can scale all the way up to 32 vCPUs and 244GB of memory.
-
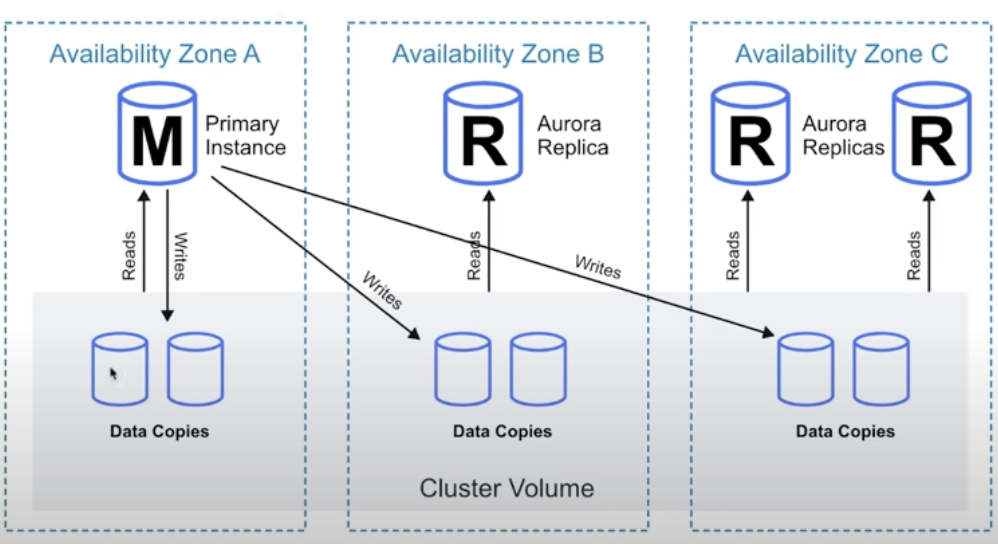
Availability with Aurora - a minimum of 3 availability zones, each contain 2 copies of your data at all time (total of 6 copies).
-
Can lose up to 2 copies of your data without affect write ability.
-
Can lose up to 3 copies of your data without affecting read availability.
-
Auorora Backup and Failover is handled automatically, self-healing
-
Replicas Two types of replicas.
-
Amazon Aurora Replicas and MySQL Read Replicas
-
Serverless - pay for database storage and the database capacity and I/O your database consumes while it is active
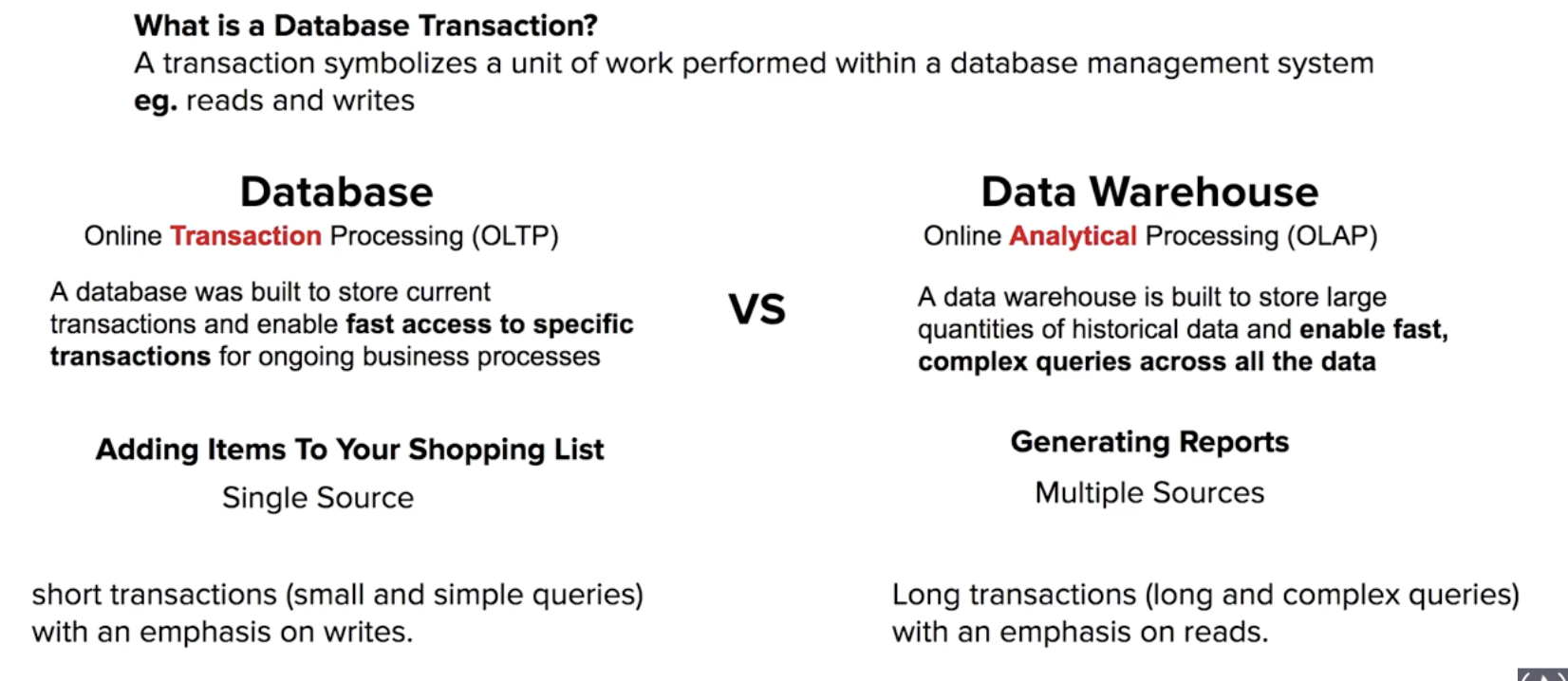
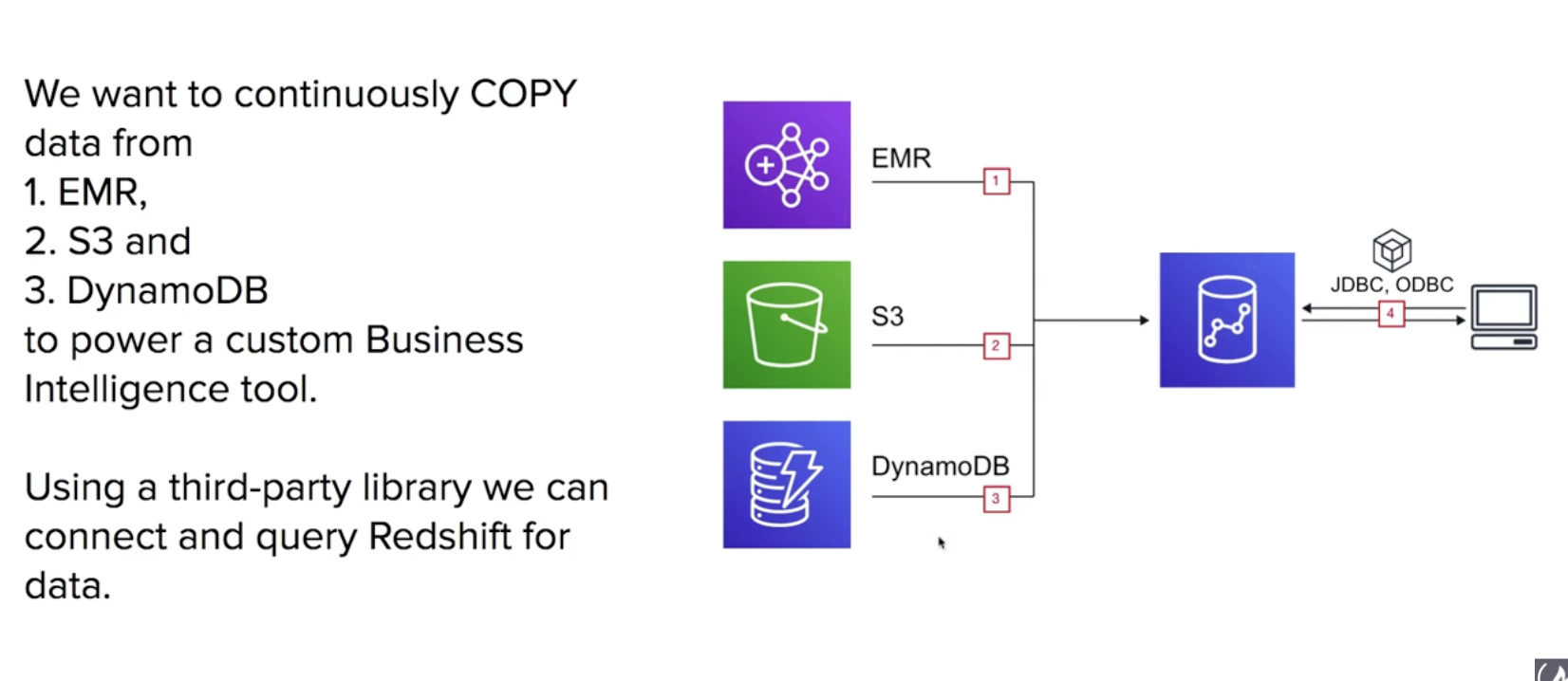
Amazon Redshift - Fully Managed Petabyte-size Data Warehouse, run complex SQL queries on massive amounts of data, is a Columnar Store database
- data insights
- takes data from multiple sources
- columnar store - database is an important factor in optimizing analytic query performance because it drastically reduces the overall disk I?O requirements and reduces the amount of data you need to load from disk
 Single Node vs Multi node
Single Node vs Multi node
- Multi node - leader node + compute node (128 max, 32 default service limit)
Dense Compute vs Dense Storage
Compression
- uses multiple compression techniques
- similar data is stored sequentially
- does not require indexes or materialized views, which saves a lot of spaces compared to traditional systems.
Processing
- Redshift uses massively parallel processing (MPP)
- automatically distributes data and query loads across all nodes
- lets you easily add new nodes to your data ware house while still maintaining fast query performance
Backups
- enabled by default with a 1 day retention period, modified up to 35 days
- always attempts to maintain 3 copies of your data.
- asynchronously replicate your snapshots in a different region to S3
Billing
- total number of hours across all nodes
- billed for 1 unit per node, per hour
- not charged for leader nodes, only compute nodes
- backups stored on S3 are also builed
- billed for only transfers with a VPC, not outside it
Security
- data in transit using SSL
- data at rest using AES-256 encryption,
- can be applied using KMS multi-tenant HSM
- CloudHSM single-tenant HSM
Availability
- Single-AZ
- but snapshots can be restored to a different AZ in event of an outage
DynamoDB a key-value and document database (NoSQL) which can guarantees consistent reads and writes at any scale.
- Fully managed
- Multiregion (stored across 3 regions on SSD)
- Multimaster
- Durable Database
- Scales - with whatever read and write capacity you specify by second
- Consistent Reads - it is possible for data to be inconsistent if you are reading from a copy which has yet to be updated.
- Eventual Consistent Reads - Default - data is returned immediately, but data can be inconsistent, copies of data will be generally consistent in 1 second
- Strongly Consistent Reads - will wait until data is consistent, but with some latency
Table Structure
- item,
- attribute
- primary key (partition key + sort key)
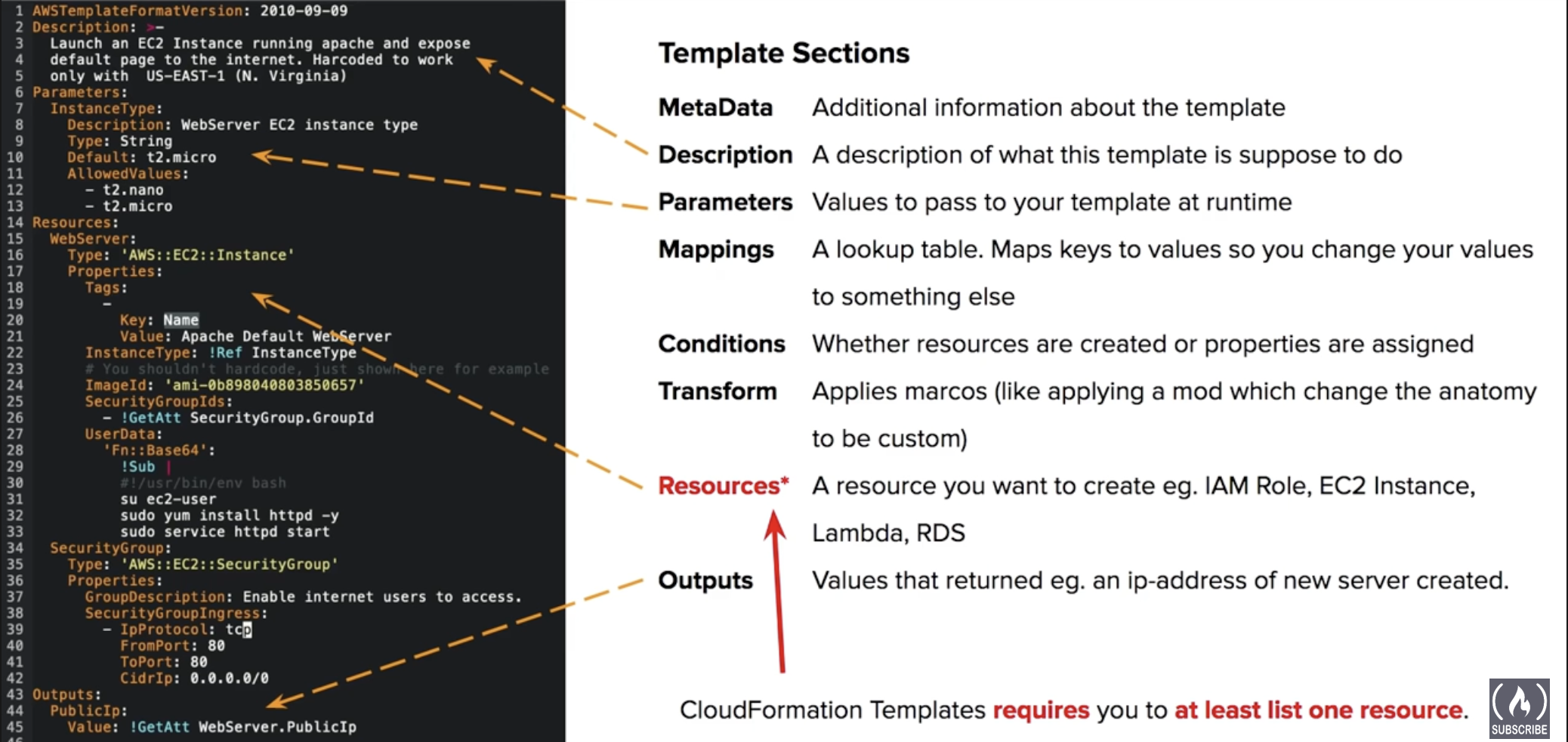
AWS Cloud Formation - infrastructure as code - a templating language that defines AWS resources to be provisioned, automating the creation of cloud
- template formats - JSON, YAML
- template anatomy - must specify at least one resource
- when it encounters an error → rollback with ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS
- greater than 0.05 MB are too large, must be imported into CloudFormation via a S3 bucket.
- Nested Stacks helps you break up your CloudFormation template into smaller usable templates that can be composed into larger templates.
AWS Quick Starts - a collection of pre-built CloudFormation templates.
Infrastructure as Code - the process of managing provisioning computer data centers (AWS) through machine-readable definition files rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools (stop doing manual configuration)
CloudWatch - a collection monitoring services for logging, reacting, and visualizing log data.
- Logs - log group is a collection of logs, log files must belong to a log group, a log in a log group is called a log stream. By default, logs are kept indefinitely and never expire. Most AWS services are integrated with CloudWatch logs. Logging of servies sometimes needs to be turned on or requires the IAM permissions
- Metrics , custom metrics can be created with AWS CLI or SDK. custom metrics can allow high resolution metrics, allows you to track 1 minute down to 1 seconds.
- Events - trigger an event based on a condition or on schedule
- Alarms - triggers notifications based on metrics when breaching a defined threshold.
- Dashboards - custom dashboards from cloudwatch metrics
EventBridge - for event notifications…
CloudWatch Availability = how often CloudWatch will collect and make available data.

Agent and Host Level Metrics - some metrics you might think are tracked by default for EC2 instances are not, and require install the CloudWatch Agent. A script which can be intaled via System Manager. Run Command onto the target EC2 instances.
Cloud Trail - longing API calls between AWS services when you need to know who to blame. Enables governance, compliance, operational auditing, and risk auditing of AWS Account. Helps you identify which users and accounts made the call to AWS e.g.
- Event History — logs by default, collet logs for the last 90 days via Event History. To track beyond 90 days, you need to create a Trail.
- To ensure logs have not been tempered with, turn on Log File Validation
- Can be encrypted with KMS.
- Trails are output to S3 and do. not ave GUI like event history. to analyze a trial you have to use Amazon Athena
- Can send Cloud Trail logs to Cloud Watch
- Management Events - tracks management operations. turned on by default, can’t be turned off.
- Data Events - track specific operations for specific AWS services, data events are high volume logging and will result in additional charges. Turned off by default.
AWS Lambda - run code without provisioning or managing servers. Servers automatically start and stop when needed. Serverless functions. Pay per innovation.
- lambda executes your code only when needed and scales automatically to a few to a 1000 lambda functions concurrently.
- commonly used to glue different services together so the use cases are endless.
- triggers - can be invoked via the AWS SDK or trigger from other AWS Services
- pricing - paid per invocation (duration and memory used)
- first 1 million requests per month are free
- there-after $0.20 per addition 1 million requests
- 400,000 GB seconds free per month
- $.00002 for every GB second
- price will vary on the amount of memory you allocate
- by default, you can have 1000 lambda running concurrently (can ask AWS support for increase)
- /tmp directory can contain up to 500MB.
- by default, lambda run in No VPC. You can set them to by in your own VPC but your lambda will lose internet access.
- you can set timeout to be a maximum of 15 minutes, if more, consider AWS Fargate
- Memory can be set between 128 to a Maximum of 3008MB at an increment of 64MB.
- By default, run in No VPC.
- Cold Starts
Simple Queuing System - application integration, is a solution for the distributed queuing of message generated by your application. It connects isolate applications together by passing along message to one another. Is PULL based.
- app publishes message to the queue
- other app pulls the queue and find the message and does something
- other app reports that they completed their task and marks the message for completion
- original app pulls the queue and sees the message is no longer in the queue.
Limits and Retention
- Message Size - size of message can be between 1 byte and 256KB
- Message Retention - message retention (time before drop) by default is 4 days, message retention can be adjusted from a minimum of 60 seconds to a max of 14 days.
- Standard Queues - nearly unlimited number of transactions, guarantees that a message will be delivered at least once. more than one copyof a message could potentially be delivered out of order, and provides best effort ordering that helps ensure a message is generally delivered in the same order that was sent.
- First-In-First Out - support multiple ordered message groups, limited to 300 transactions per second
- Visibility Timeout - period of time that messages are invisible in the SQS queue, after a reader picks up that message. Default is 30 seconds, range from 0 seconds to 12 hours.
Short vs Long Polling
- Short Polling - default, returns messages immediately, even if the message queue being polled is empty, good when you need message right away.
- Long Polling - waits until message arrives in the queue or the long poll time out expires. makes it inexpensive to retrieve message from your queue as soon as the messages are available. reduce cost because you reduce the number of empty recieves. → majority cases long polling is preferred over short polling.
Simple Notification Service - subscribe and send notifications via text message, email,
- Pub/Sub - publish subscribe pattern. Publishers send message to event bus, which categorizes their messages into groups. Then receivers of messages (subscribers) subscribe to these group.
- Application integration, fully managed, durable, secure
- Can encrypt topics via KMS.
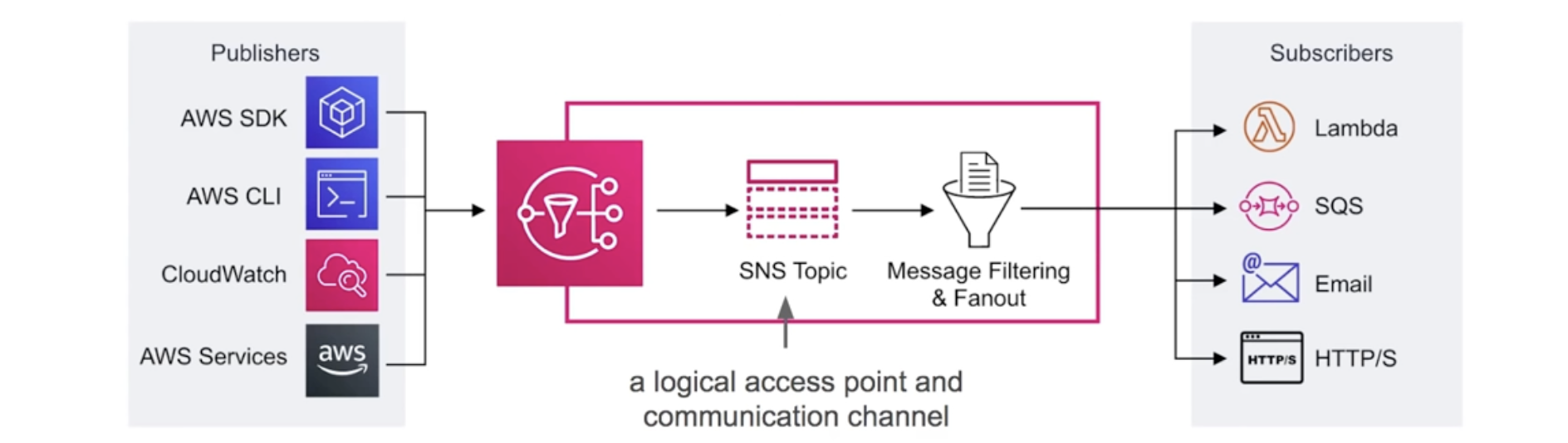
- SNS Topics - allow you to group multiple subscriptions together. when topics deliver messages to subscribers, it will automatically format your messages according to the subscriber’s chosen protocol.
ElastiCache - managed caching services that run on Redis or Memcached
- in memory data store - fast access but high volatility
- is only accessible to resources operating with the same VPC to ensure low latency.
- Memcached - preferred for catching HTML
- Redis -
High Availability Architecture - the ability for a system to remain available.
- Understand situations that could cause a service to become available.
- Find solutions to implement high availability.
- scale up vs scale out
Elastic Beanstalk - powered by a CloudFormation template. Not Recommended for “production applications”.
- Choose a platform, upload your code and it runs with little worry for developers about infrastructure knowledge.
- Handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling to application health monitoring
- can run dockerized environments
API Gateway - fully managed service to create, publish, maintain, monitor and secure APIs at any scale.
- Create APIs that act as a front door for applications to access data, business logic, or functionality from back-end services.
- Hundreds of thousands of concurrent API calls, including traffic management, authorization, and monitoring
- Allows you to track and control any usage of the API, throttle requests to help prevent attacks
- Highly scalable (automatic)
- Send each API endpoint too a different target
- Maintain multiple versions of your API.
- Can require authorization to your API via AWS cognito or custom Lambda.
Configuration
- Resources - the urls you define, can have child resources
- Methods - specifying the protocol
- Stages - stages are versions of your API
- Invoke URL - for each stage, AWS provides a Invoke URL. This is where you’ll make your API calls.
- Deploy API - every time you make a change to your API you need to Deploy it via the Deploy API actions.
Caching - enable cache to endpoints response to API calls
- API caches responses from your endpoint for a specified TTL.
- API Gateway responds to request by looking up responses in the Cache, saves money.
- CORS - Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) - is a way that the server at the other end (not client code in the browser) can relax a same-origin policy.
- protects us from XSS attacks
- But what if we want to access things from another domain name.
- by default not turned on.
- Allows restricted resources (i.e. Fonts) on a webpage to be requested from a different domain than the initial resource that it came from.
- Should always be enabled if using Javascript/AJAX that uses multiple domains with an API gateway.
- CORS is always enforced by the client
Same Origin Policy - a concept in the application security model where a web browser permits scripts contained in a first web page, to access data in a second web page.
- Same Origin Policies are used to help prevent Cross-Site Scripting XSS attacks.
- They only works if both web pages have the same origin.
- They are enforced in browsers.
- Ignore tools like postman or curl
Amazon Kinesis - scalable and durable real-time data streaming service. To ingest, and analyze data in real-time from multiple source.
- Examples - stock prices, game data, social network data, geospatial data, click stream data.
- Kinesis Producer Library (KPL) is a Java library to write data to a stream. You can write data to a stream using AWS SDK, but KPL is more efficient,
Kinesis Data Streams
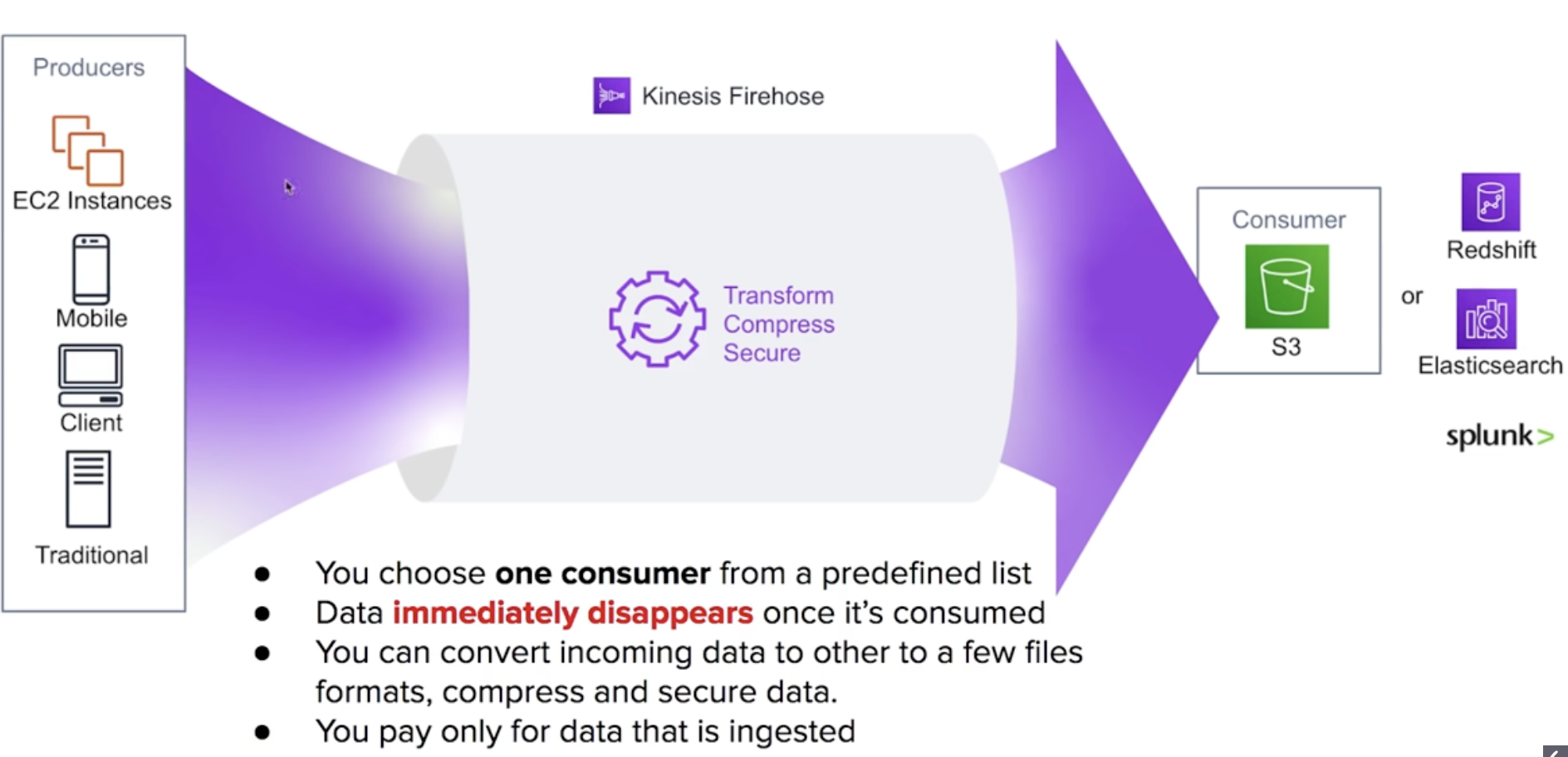
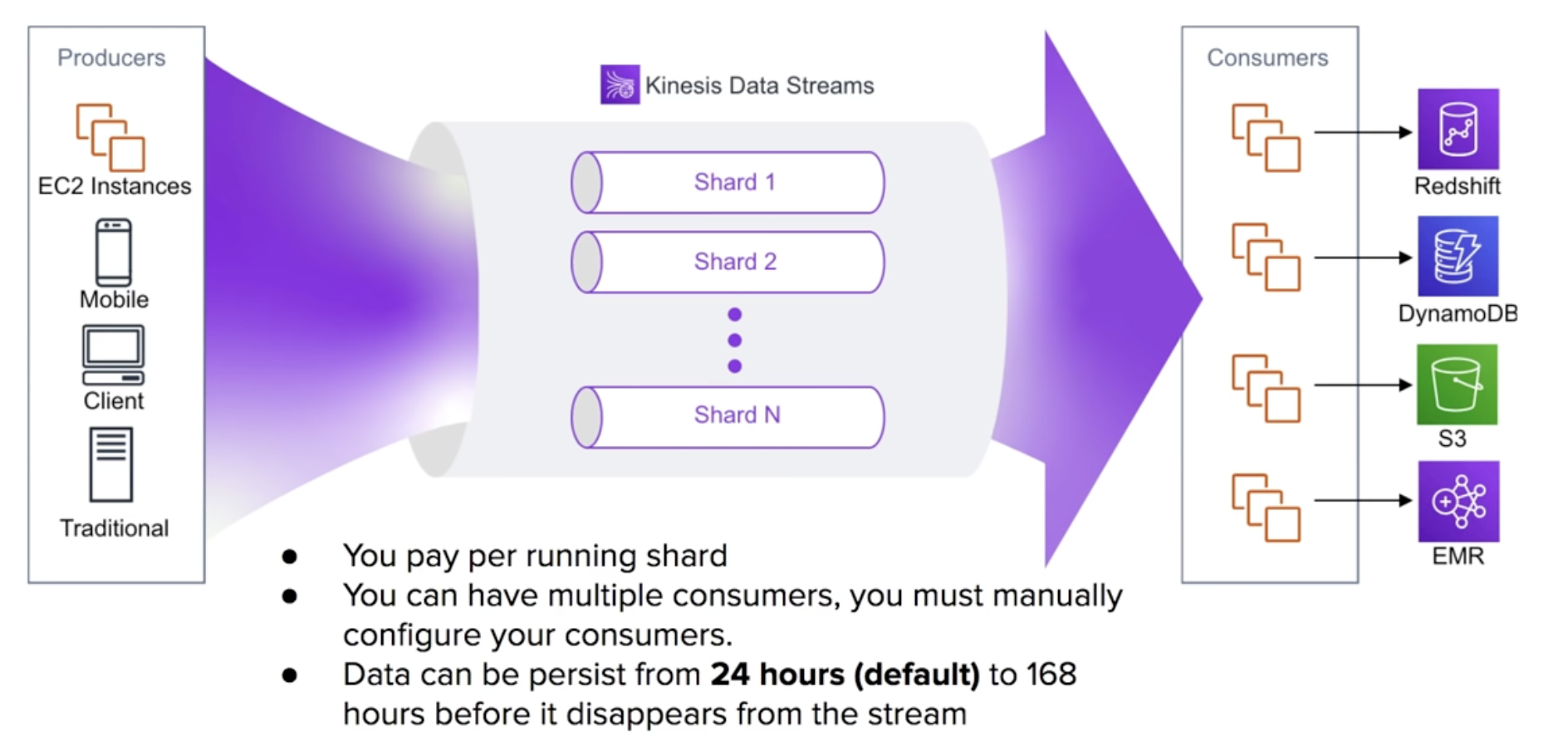 Kinesis Firehose Delivery
Kinesis Firehose Delivery
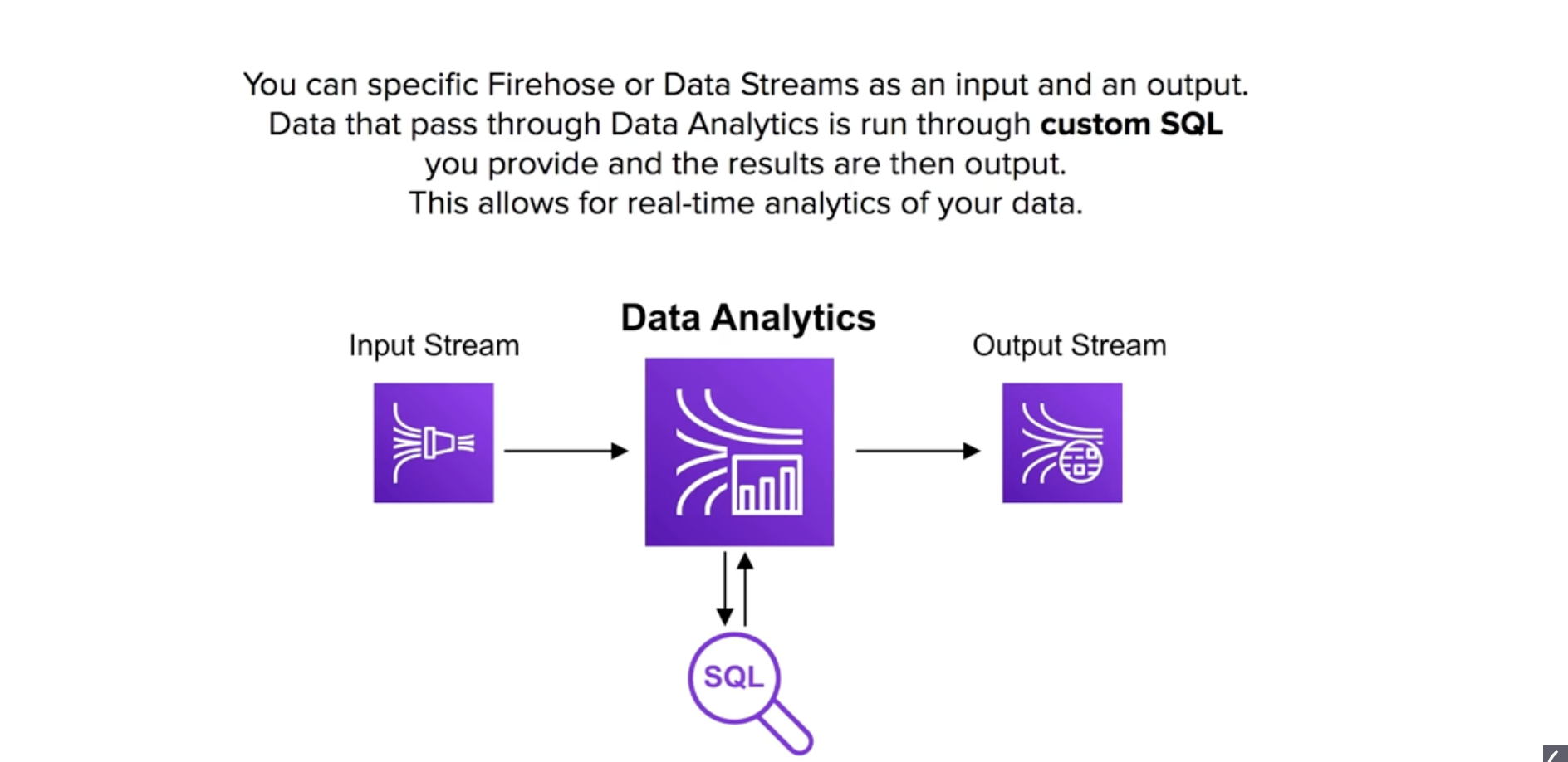
 Kinesis Data Analytics
Kinesis Data Analytics
Kinesis Video Analytics

AWS Storage Gateway - extending, backing up on premis storage to the cloud.
- securely store your data to the AWS cloud for scalable and cost effective storage.
- File Gateway (NFS) - files are stored as objects inside your S3 buckets. Access your files through a Network File System (NFS) or SMB mount point.
- Volume Gateway (iSCSI) - presents your applications with disk volumes using Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) block protocol.
- data that is written to the volumes can be asynchronously backed up as point-in-time snapshots and stored in cloud as AWS EBS Snapshots.
- Snapshots are incremental backups for only changed blocks
- Compressed Snapshots.
- Stored Volumes - primary data is stored locally, while asynchronously backing up the data to AWS through EBS Snapshots (stored volumes are 1GB to 16TB)
- Cached Volumes - caches frequently used files on premisis. Primary data is stored on S3 (stored volumes are 1GB to 32GB)
- Tape Gateway (VTL) - durable, cost effective, store data on virtual tape cartridges that you create on your tape gateway.
- each tape gateway is pre-configured with a media changer and tape drives, which are available to your existing client backup application as iSCSI devices.
- You can add tape cartridges as you need to archive your data.
- Backups to virtual tapes to S3 glacier for long archive storage