AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
My notes for the AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials certification https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-cloud-practitioner/.
Table of Contents
00 Plan of Attack
Important Resources
- Homepage - https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-cloud-practitioner/
- AWS Services - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/introduction.html
Learning
- Cloud Essentials - Knowledge Badge Readiness Path
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Certification Course (CLF-C02)
Practicing
- Exam Prep Official Question Set: AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02 - English)
- Exam Prep Standard Course: AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02 - English
- https://github.com/kananinirav/AWS-Certified-Cloud-Practitioner-Notes/tree/master
01 Key Takeaways
AWS is a Cloud Service Provider (CSP).
- No longer need to buy the infrastructure… paying only for what you need
- On demand delivery and cloud deployments, pay as you go pricing model
- Benefits of AWS Cloud Computing
- trade upfront expense for variable expense
- stop spending money to run and maintain data centers
- stop guessing capacity
- benefit from massive economies of scale
- increase speed and agility
- go global in minutes
Key-terms
- Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
- Technical Account Manager (TAM)
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- AWS DAX Accelerator
- AWS Service Control Policies (SCP)
Cloud Service Provider if an organization has the skills to build and manage its cloud environment and solutions itself, then it may only want to access the sstandard cloud services from the CSP, like AWS or a cloud reseller
Cloud Adoption Parts
- Procurement - pricing, security, data soveriengty/residency, sustainability, governance, terms and conditions
- Legal
- Security
- Governance
- Finance
- Compliance
AWS Partner Network The AWS Partner Network (APN) is a global community of partners that leverage Amazon Web Services (AWS) to build solutions and services for customers. The APN helps companies build, market, and sell their AWS offerings by providing valuable business, technical, and marketing support. The network is divided into two primary types of partners: Consulting Partners and Technology Partners. Each plays a unique role in the AWS ecosystem.
- Consulting Partners - Consulting Partners are professional services firms that help customers of all types and sizes design, architect, build, migrate, and manage their workloads and applications on AWS.
- Technology Partners. Technology Partners provide hardware, connectivity services, or software solutions that are either hosted on, or integrated with, the AWS platform.
Payment Options
- On-demand - only pay for the duration the instance runs for
- Saving’s plan - low prices in exchange for consistent amount of usage measured in dollars per hour for a one or three year term (up to 72%)
- Reserved Instance - suited for steady-state workloads or ones with predictable usage and offer you up to a 75 versus On-Demand pricing. You qualify for a discount once you comit to a one or a three-year term and can pay for them with three payment options (all upfront, partial upfront, and no upfront). Require you to specify instance family and size, platform, tenancy, and region. Reserved Instances are a billing discount that is applied to the use of On-Demand Instances in an AWS account. A business can purchase Standard Reserved and Convertible Reserved Instances for a 1-year or 3-year term. Unlike EC2 Instance Savings Plans, Reserved Instances do not require an hourly spend commitment over the duration of the contract term - stndard reserve instances allows you to modify the AZ, scope, networking type, and instance size (within the same instance type)
- Convertible Reserved Instance - enables you to exchange one or more convertible reserved instances for another convertible reserved instance with a different configuration, including instance family, operaing systems, and tenancy
- Spot Instances - allow you to request spare Amazon EC2 computing capacity for up to 90% off of the O-nDemand price. The catch here is that AWS can reclaim the instance at any time they need it, giving you a two-minute warning to finish up work and save state. You can always resume later if needed. So when choosing Spot Instances, make sure your workloads can tolerate being interrupted. A good example of those are batch workloads, access to unused EC2 capacit
- Dedicated Hosts - Physical hosts dedicated for your use of EC2. Scaling Amazon EC2
- Scalability and Elasticity - growth and shrink of capacity
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling enables you to automatically add or remove Amazon EC2 instances in response to changing application demand.
- Dynamic Scaling responses to changing demand
- Predictive Scaling automatically schedules the right number of Amazon EC2 instances based on predicted demand.
- Minimum, Desired, and Maximum Capacity
- Scaling Up → more power to the machines that are running.
- Scale out →
02 AWS Shared Responsibility Model
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model … Its whitepaper can be found here https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-risk-and-compliance/shared-responsibility-model.html
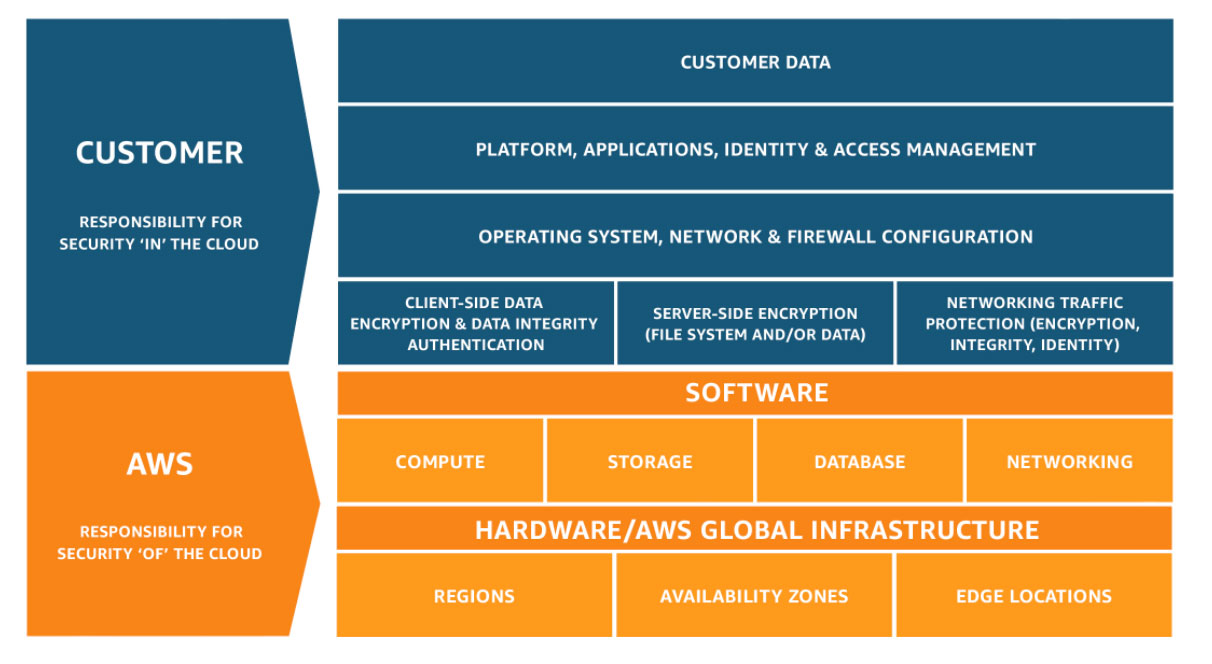 User Responsibilities
User Responsibilities
- Client-side security encryption
- update/patch the guest os on deployed EC2 instances, updating the database engine
- configure new resources within an AWS
- design a customer’s application for disaster recovery
- encrypting customer dataprovide a key for S3 side client encryption
- defining network firewalls inside VPC AWS Responsibilities
- Security of edge locations
- Control the environment of physical AWS, Hardware security within AWS Region, secure the physical infrastructure
- AWS global infrastructure network security
- Patching and updating the hypervisor
AWS Shared Controls
- Patch Management, Configuration Management,,,,,,
Which of the following controls do customers fully inherit from AWS? - Environment Control, Physical Control
03 Well Architecture Framework
More info can be found here link White paper can be found here https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/framework/welcome.html
There are six pillars to WAF:
- Operational Excellence - This pillar, notifiy users when they are impacted by events, ability to monitor systems and improve supporting processes and procedures.
- Security - The Security pillar helps customer with design principles to enable traceability, apply security layers, protect data in transit and at rest, automate security best practices and prepare for security events.
- Reliability - The reliability pillar focuses on workloads performing their intended functions and how to recover quickly from failure to meet demands. Key topics include distributed system design, recovery planning, and adapting to changing requirements.
- Performance Efficiency
- Cost Optimization
- Sustainability
Benefits to WAF include:
- reduce and mitigate risks
- build and deploy faster
, There is a WAF Tool…
04 Cloud Adoption Framework
Whitepaper ca be found here - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/overview-aws-cloud-adoption-framework/welcome.html?did=wp_card&trk=wp_card
Cloud Adoption Framework - Provides advice to company to enable a quick and smooth migration to AWS. Guidance is organized in 6 perspectives helping these groups of people in migration - Business - Business Managers, Finance Managers, Budget Owners, Strategy Stakeholders - People - HR, Staffing, People Managers - Governance - - Platform - - Security - Traceability - Protect data in transit and at rest - Operation - focuses on recovering IT workloads to meet the requirements of business stakeholders
Cloud Adoption Strategy -
- Procurement - pricing, security, data soveriengty/residency, sustainability, governance, terms and conditions
- Legal
- Security
- Governance
- Finance
- Compliance
05 AWS Global Infrastructure
In order to provide high availability and fault tolerance, aws operates in all sort of different areas called regions. Each region is connected to another region through high speed fiber network, and within each region, there are multiple data centers (or multiple groups of data centers) called availability zones. Users, when launching instances, get to choose which region and zone their services operate in.
- availability zones - regions are made up of multiple data center, one single or group of data center is called a availability zone, availability zones are spread out across the region in case of disasters. run multiple EC2 instances in different availability zones (recommended at least two)
- What if you have customers all over the world? some customers might not be close to the main data to
- caching copies of data closer to the customers all aroudn the world → Content Delver Networks (CDN) - Amazon Cloudfront Helps deliver data to custoemrs around the world
- Amazon Cloudfront also run a DNS called Amazon Route 53, helping direct customers to the correct web locations with low latency.
- AWS Outposts - AWS install a fully operationall mini region in your own data centers, isolated to a single building.
AWS Networking
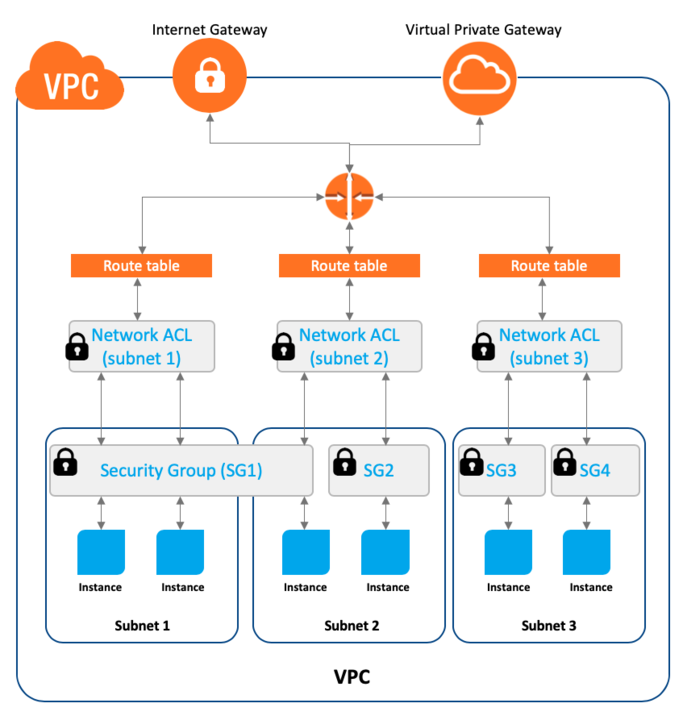
- These resources can be public facing so they have access to the internet, or private with no internet access.
- public vs private subnet
- allows you define private ip range for AWS resources
- subnets allow you to group services together.
- subnets must stay entirely within one availability zone
Internet Gateway - public facing
- provide a target in your VPC routing table for internet routable traffic
- perform NAT for instances that have been assigned IPv4 address Virtual Private Gateway - VPN connection from
- private but still use regular connection, share bandwith with other people using internet Network Access Control Lists - stateless (checks all packets regardless of any circumstance) → every ingress/egress packets all checked, initially allows all ingress/outgress. Also performs DDOS prevention, Data Integrity, Encryption, Authentication and Authorization Access Control Lists Security Groups - By default, security group blocks all ports, preventing traffic and must be modified to allow inbound/outbound. It is stateful, meaning it allows all return traffic without having to recheck list.
Account Management
- AWS account root user → owner of aws account, permission to do anything, recommended to turn on multi-factor authentication (MFA) for root user
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) By default, a new user has zero permission (not even logging in), give granular permissions to all users
- Least privlage principle - users are granted IAM policy to an IAM user, a JSON document which describes API calls a user can or cannot make.
- IAM Policy - a document that allows or denies permissions to AWS services and resources.
- IAM Groups - attaching policies to groups of users
- IAM Roles - associated permissions that allowr or deny, assumed for temporary amounts of time, no users or passwords, access to temporary permissions to AWS resources, users, external identities, applications, or other AWS services. When an identiy assumes a role, it abondons all previous permissions.
- Task Role
- Web Identity Role
- Service Role
- Instance Role - Grant acess to specific instances
- Identity Federation - allow existing identities (users, groups, and roles) in your enterprise to access the AWS Management Console, call AWS APIs, and access resources, without the need to create an IAM user for each identity.
Do not use the root user for everyday tasks
Instead, use the root user to create your first IAM user and assign it permissions to create other users. Only use the root user for specific tasks.
Practices
- rotate credentials regularily
- enable multi-factor authentication
- delete all root user keys
Identities
- Roles
- Groups
AWS Organizations
- a central location to manage multiple AWS accounts.
- consolidated billing
- hierarchical groupings of accounts
- AWS service and API actions access control for each individual user- Service Control Policies (SCPs) - can be applied to an individual member account or an organizational unit (OU)
- volume discounts
Compliance
- Ex Regulations- General Data Protection Regulation in Europe, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act in US
- AWS has already built out data center infrastructure and networking following industry best practices for security, and as an AWS customer, you inherit all the best practices of AWS policies, architecture, and operational processes.
- AWS assurance programs
- AWS Compliance - information about compliance services and documents
- Coustomer Complience Cente
Migration and Innovation
Migration and Innovation Migration Strategies The 6 R’s - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/enterprise-strategy/6-strategies-for-migrating-applications-to-the-cloud/
- Rehosting - lift and shift, pick and move applications as is to aws
- Replatforming - lift, tinker, and shift, make a few cloud optimizations, no new applications changes / no code changes, such as moving local mysql to RDS mysql
- Retire - turn off deprecated / unused parts of the application
- Retain - migrate only what makes sense
- Repurchasing - abandon legacy software vendors and moving to a new one
- Refactoring - rewriting code and dramatic changes to architectr
04 Services
This is not a complete list! A more complete list can be found here link.
Compute
Compute as a service (CaaS) model
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) - EC2 service allows to work with virtual servers that provide the raw compute capacity to host application needs.
- Configuration
- Operating System
- Software
- Resizable
- Networking
- Types of Instances - Each Amazon EC2 instance type is grouped under an instance family based on task, offering different variations of cpu, memory, networking resources.
- General Purpose - balanced, diverse workloads
- Compute optimized - compute intensive tasks - gaming servers, HPC, scientific modeling, batch processing
- Memory optimized - memory intensive
- Accelerated Computing - floating point number calc, graphics processing, data pattern matching
- Storage Optimized - high performance for locally stored dat
- Payment Options -
- On-demand
- Savings Plan
- Reserved
- Standard Reserved
- Convertible Reserved
- Spot Instance
- Dedicated Hosts
- Configuration
- AWS Lambda - AWS Lambda is a serverless option with following steps (1) upload your code into what is called a lambda function (2) configure a trigger, and the service waits for trigger (3) When trigger is detected, the code is run in a managed environment (automatically scalable, managed by AWS). Meant for programs under 15 mins (4) pay only for the compute time you use and the number of requests to your functions It provides per millisecond pricing of the code, and can run on either on schedule or in response to events. Like EC2, also has savings plan
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk - Elastic Beanstalk deploys and scales web applications and services. First, you upload your code to Elastic Beanstalk. Then, Elastic Beanstalk automatically manages the deployment. Additionally, Elastic Beanstalk manages capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto scaling, and application health monitoring.
- Amazon Fargate - Fargate is a serverless service that you can use with Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS). You can use Fargate to run containers without the need to manage servers or clusters of Amazon EC2 instances.
- AWS Batch - AWS Batch lets developers, scientists, and engineers across industries efficiently run hundreds of thousands of batch computing jobs while optimizing compute resources, providing the ability to focus on analyzing results and solving problems.
- AWS Lightsail - Basically a VPS, better for Dynamic Websites compared to hosting static on S3.
- AWS Wavelength - AWS Wavelength embeds AWS compute and storage services within 5G networks, providing mobile edge computing infrastructure for developing, deploying, and scaling ultra-low-latency applications
- AWS Local Zones - AWS Local Zones are a type of infrastructure deployment that places select AWS services closer to your end users and workloads.
Storage
- Instance Stores Volumes - Physically attached to host EC2 is running on top of it, can write to it just like a normal hard drive. However, if EC2 terminated, volume is also terminated.
- Amazon Elastic Block Store - Storage devices that can be attached to EC2 instances that are separated from Instance Stores Volumes and not attached to the host EC2 instance is on, it can persist and comes in all different types sizes and other configurations. Reduce cost by deleting snapshots and type of volume, automatically replicated in AZ. Does not automatically scale.
- Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) - A managed file systems, multiple instances can access the data in EFS at the same time (multi instance read and write, redundantly stored across activity zones and automatically scales
- Amazon FSx - Amazon FSx provides fully managed (shared) third-party file systems with the native compatibility and feature sets for workloads such as high-performance computing (HPC), machine learning, media data processing, and financial modeling. Amazon FSx is designed to offer high levels of throughput, IOPS, and consistent low latencies. Currently, Amazon FSx supports several file system options, Lustre, WFS, ONTAP, and ZFS.
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) - S3 is an object based storage. Data is stored as objects in buckets (i.e file is object, bucket is file directory), where the object contains not only the data (value), but a key, version ID, and metadata.
- You can store and retrieve an unlimited amount of data. But each object has a maximum object size of 5TB.
- Automatically scales in size. You can create multiple buckets, give permissions to each objects. S3 is the most cost effective option to store static images, because you only pay for what you use. It’s also good for hosting static websites. It also automatically scales in throughput.
- S3 is a universal namespace so bucket names must be unique.
- Other Concepts
- Lifecycle Policies - Set rules to transition objects to different storage classes, automatically move data between tiers
- Bucket Versioning - Bucket versioning gives you the ability to maintain multiple versions of an object in an S3 bucket.
- S3 Access Points - Simplify access to a subset of objects in a bucket
- S3 Transfer Acceleration - Takes advantage of Amazon CloudFront’s globally distributed edge locations to transfer files to S3 with higher upload speeds
- Amazon S3 Standard — 99.999999999% of durability after a period of 1 year, aws can sustain the concurrent loss of data in at least 2 seperate facillities bc data is stored in at least 3 fascilities
- Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard IA) - good for data access less frequently but requires rapid data when leader - good for backups, distaster recovery files, good for long term storage
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering - ideal for unpredictable access patterns, requires a small monthly monitoring and automation fee per object - monitors object access patterns. If object has not been accessed for 30 cosecutive days, moves it to the infrequent access tier, if object is, it is move to the frequent access tier, S3 standard
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval - works well for archived data that requires immediate access, can retrieve objects within a few milliseconds
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval - make vaults, populate archives, can lock the vaults, can implement policies such as WORM.
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive - lowest cost object storage class ideal for archiving, able to retrieve objects within 12 hours.
- S3 Outposts - S3 buckets on S3 outposts
- One Zone-IA
- AWS Storage Gateway - AWS Storage Gateway gives your applications on-premises and in-cloud access to virtually unlimited cloud storage.
- AWS Backup - AWS Backup lets you centrally manage and automate backups across AWS services and third-party applications.
- AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery - AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery (AWS DRS) minimizes downtime and data loss with fast, reliable recovery of on-premises and cloud-based applications using affordable storage, minimal compute, and point-in-time recovery.
Database
- Relational
- RDS - Fully managed relational database, uses EBS as primary storage, resizable compute compacity. Can host MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server databases. It provides automated patching, backups, redundancy, failover, disaster recovery. Will launch in the primary AND standby databases in different Availability Zones
- Amazon Aurora - Amazon Aurora is a enterprise class relational database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL. Extremely cheap, about 1/10th the cost of commercial databases. Fully managed by RDS. Is self-healing, distributed, fault tolerant
- Data replication (6 copies) across facilities, 15 read replicas, continuous backups to Amazon S3, point-in-time recovery.
- You remain ownership of data, schema, but has some overhead which is necessary if you need complex relationships.
- Redshift - Amazon Redshift is a data warehousing as a service, query and analyze data cross a data warehouse. Works in cooperation with Amazon Redshift Spectrum, which can run a single SQL query against exabytes of unstructured data running in data lakes. Uses a variety of innovation 10x higher performance than traditional databases when it comes to Business Intelligent workloads
- Key-value
- Amazon Dynamo DB - NoSQL (jet-value) , provides single-digit millisecond performance at any scale, automatically scales with Auto Scaling meet throughput capacity, serverless database, fully managed.
- In-memory
- ElasticCache - is a fully managed in-memory data caching service for databases.
- Amazon MemoryDB for Redis
- Document
- DocumentDB w/ MangoDB
- Wide Column
- Amazon Keyspace
- Graph
- Amazon Neptune - Graph Database, Managed
- Time Series
- Amazon Timestream
- Ledge
- Amazon Ledger Database Service (QLDB) - Immutable, entries cannot be removed
Network
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) - Amazon Virtual Private Cloud allows you to provision a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define. These resources can be public facing so they have access to the internet, or private with no internet access. public vs private subnet. allows you define private ip range for AWS resources, subnets allow you to group services together. subnets must stay entirely within one availability zone
- Site-to-Site VPN - Site-to-Site VPN creates encrypted tunnels between your network and your Amazon Virtual Private Clouds or AWS Transit Gateways. Requires Customer Gateway and Transit Gateway
- Client VPN
- Peering Connection - A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. Not good for managing many VPC to VPC connections. Instead, use AWS Transit Gateway.
- Direct Connect - Private, dedicated fiber connection between (on premises network) data center and to AWS Cloud (VPC), however communication is not encrypted!
- Amazon Route 53 - Amazon’s Domain Name Service (DNS) which translates website names to ip protocol. Has a bunch of different routing policies. It provides health checks (detecting outage), which can either provide latency-based routing or redirection to alternate service. You can also register and buy domain names.
- Amazon CloudFront - CDN, network that delivers edge content to users based on their geographic location. Also provides DDoS.
- AWS VPN - AWS VPN establishes a secure encrypted connection between AWS and your premises or branch-office networks.
- AWS Global Accelerator - AWS Global Accelerator is a networking service that helps you improve the availability, performance, and security of your public applications. Global Accelerator provides two global static public IPs that act as a fixed entry point to your application endpoints, such as Application Load Balancers, Network Load Balancers, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances, and elastic IPs.
Security, Identity, and Compliance
Security
- Amazon Macie - Amazon Macie is a security service that uses machine learning to discover and protect sensitive data stored in the cloud. It can be used to secure sensitive data stored in the cloud by identifying and alerting on any unauthorized access or breaches.
- Amazon GuardDuty - Amazon GuardDuty provides intelligent threat detection for AWS infrastructure and resources
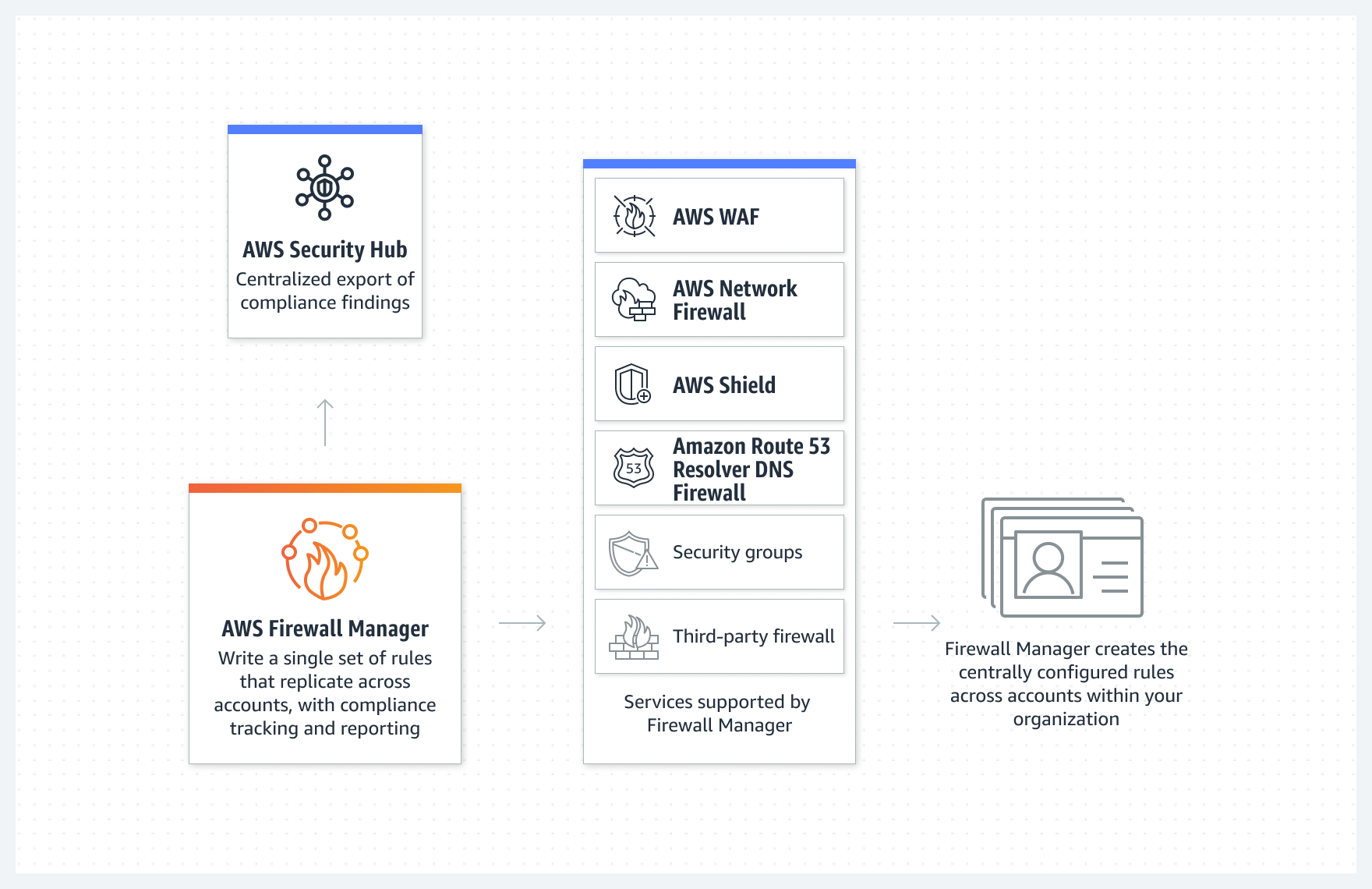
- Amazon WAF - AWS WAF is a web application firewall that helps protect your web applications from common web exploits that could affect application availability, compromise security, or consume excessive resources. For example, prevents SQL Injection attacks.
- Amazon Inspector - Amazon Inspector scans AWS workloads, including Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) container images, and AWS Lambda functions. Amazon Inspector scans these workloads for software vulnerabilities and unintended network exposure. Generally for security!
- Amazon Detective - Amazon Detective simplifies the investigative process and helps security teams conduct faster and more effective investigations. With the Amazon Detective prebuilt data aggregations, summaries, and context, you can quickly analyze and determine the nature and extent of possible security issues.
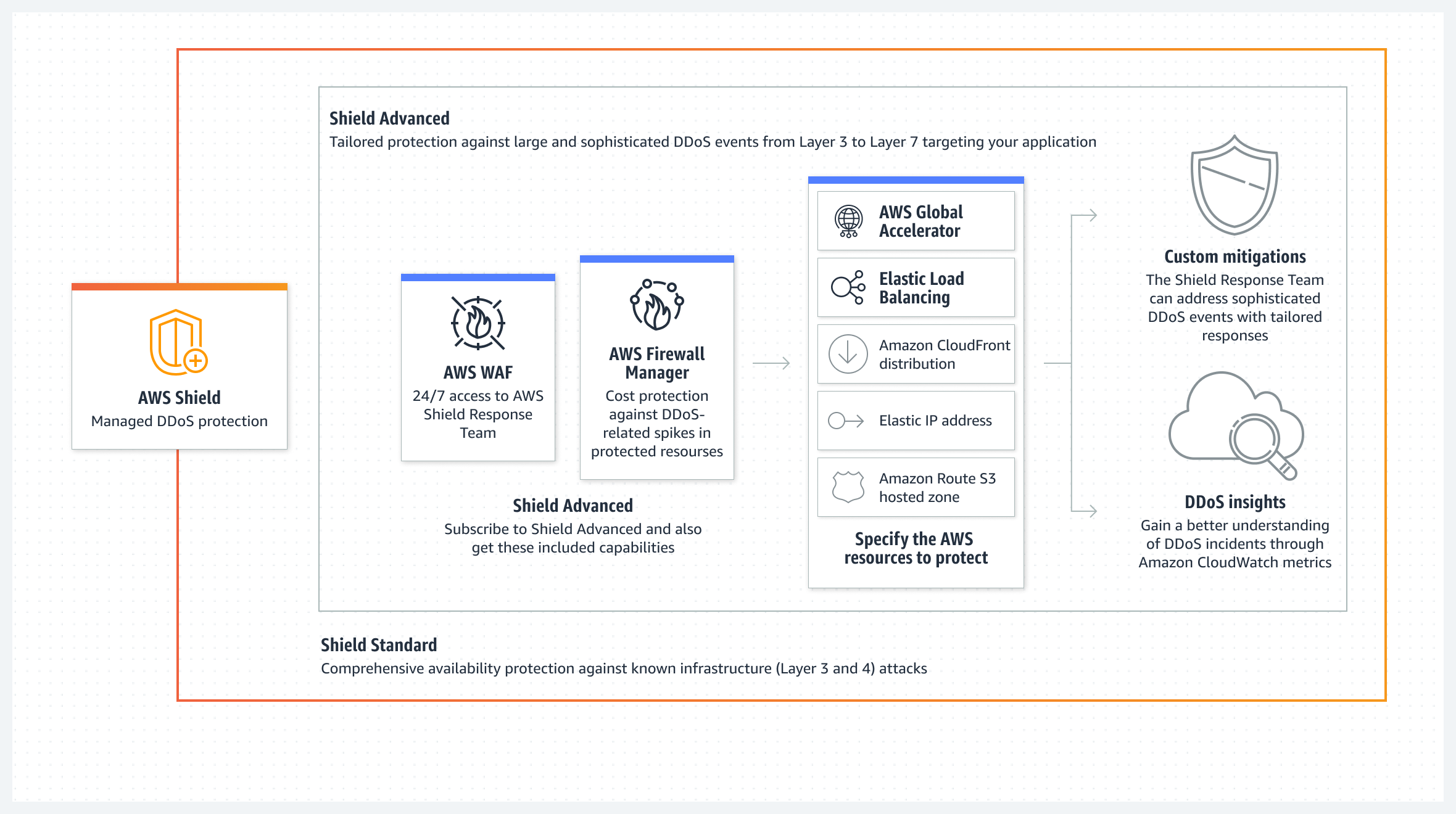
- Amazon Shield - AWS Shield is a managed DDoS protection service that safeguards applications running on AWS.
- AWS Security Hub
- Amazon Firewall Manager - AWS Firewall Manager is a security management service that allows you to centrally configure and manage firewall rules across your accounts and applications in AWS Organizations. As new applications are created, Firewall Manager makes it easier to bring new applications and resources into compliance by enforcing a common set of security rules.
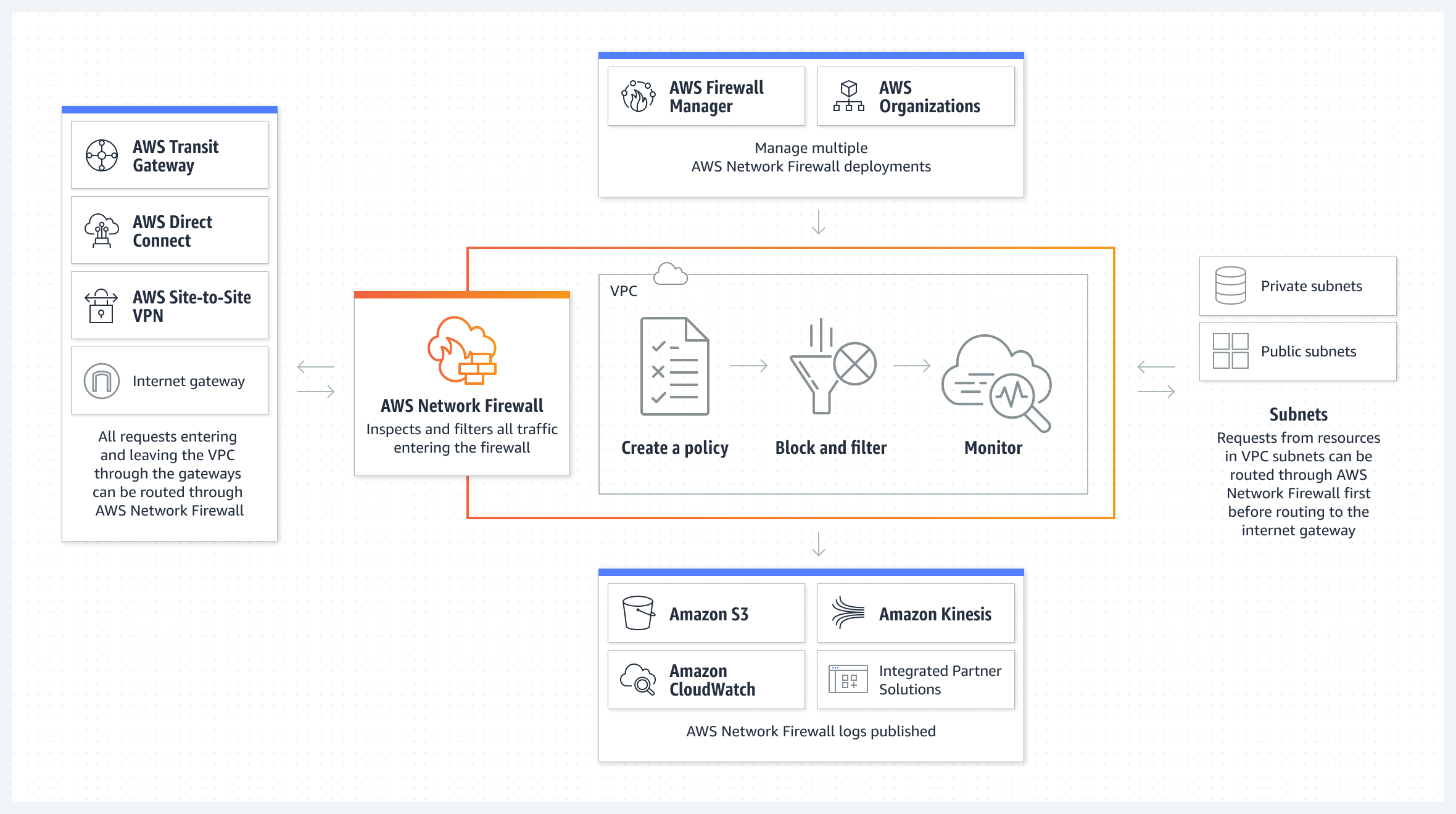
- Amazon Network Firewall - AWS Network Firewall allows you to define firewall rules that provide fine-grained control over network traffic. Network Firewall works together with AWS Firewall Manager so you can build policies based on Network Firewall rules and then centrally apply those policies across your virtual private clouds (VPCs) and accounts.
- Also performs traffic flow inspection and traffic filtering.
- Amazon Cloud Directory - Amazon Cloud Directory allows the organization of hierarchies of data across multiple dimensions.
- AWS Directory Service - Microsoft Active Directory, also known as AWS Managed Microsoft AD, enables your directory-aware workloads and AWS resources to use managed Active Directory in the AWS Cloud.
- AWS CloudHSM - AWS CloudHSM is a cloud-based hardware security module (HSM) that enables you to easily generate and use your own encryption keys on the AWS Cloud.
Identity
- AWS Resource Access Manager - RAM helps you securely share your resources across AWS accounts, within your organization or organizational units (OUs), and with IAM roles and users for supported resource types.
- AWS Secrets Manager - AWS Secrets Manager helps you manage, retrieve, and rotate database credentials, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycles.
- AWS Cognito - AWS Cognito helps implement secure, frictionless customer identity and access management that scales.
Analytics
- Amazon Athena - Amazon Athena is a serverless, interactive analytics service that provides a simplified and flexible way to analyze petabytes of data where it lives (for example, query on S3 data directly). It is good for both complex and simple queries.
- Amazon QuickSight - QuickSight is a business intelligence service that delivers insights with dashboards.
- Amazon Elastic MapReduce (EMR) - Amazon EMR is a cloud big data platform for running large-scale distributed data processing jobs, interactive SQL queries, and machine learning applications. Fully managed.
- AWS Data Exchange - Data Exchange allows you to easily find, subscribe to, and use third-party data in the cloud. Basically a Data Marketplace.
- AWS Glue - Glue is a serverless data integration service that makes it easier to discover, prepare, move, and integrate data from multiple sources for analytics, machine learning (ML), and application development.
- Amazon Kinesis Amazon Kinesis cost-effectively processes and analyzes streaming data at any scale as a fully managed service. With Kinesis, you can ingest real-time data, such as video, audio, application logs, website clickstreams, and IoT telemetry data, for machine learning (ML), analytics, and other applications.
- Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK) - Amazon MSK makes it easy to ingest and process streaming data in real time with fully managed Apache Kafka.
- Amazon OpenSearch - Amazon OpenSearch Service makes it easy for you to perform interactive log analytics, real-time application monitoring, website search, and more. OpenSearch is an open source, distributed search and analytics suite derived from Elasticsearch.
Management and Governance
- Amazon CloudWatch - Amazon CloudWatch monitors your Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time.
- Alarms - Create billing alarms
- Amazon CloudFormation - Amazon CloudFormation is infrastructure as code tool, used to define a wide variety of AWS resources in a declarative way using
jsonoryamlcalled cloud formation templates which state what you want to build while the cloud formation enginer decides how it is built. Built in parallel. automated process. “treat your infrastrcuture as code” - Amazon CloudTrial - Track API Calls
- Trusted Advisor - Checks instances against best practice pillars: cost optimization, performance, security, fault tolerance, service limits
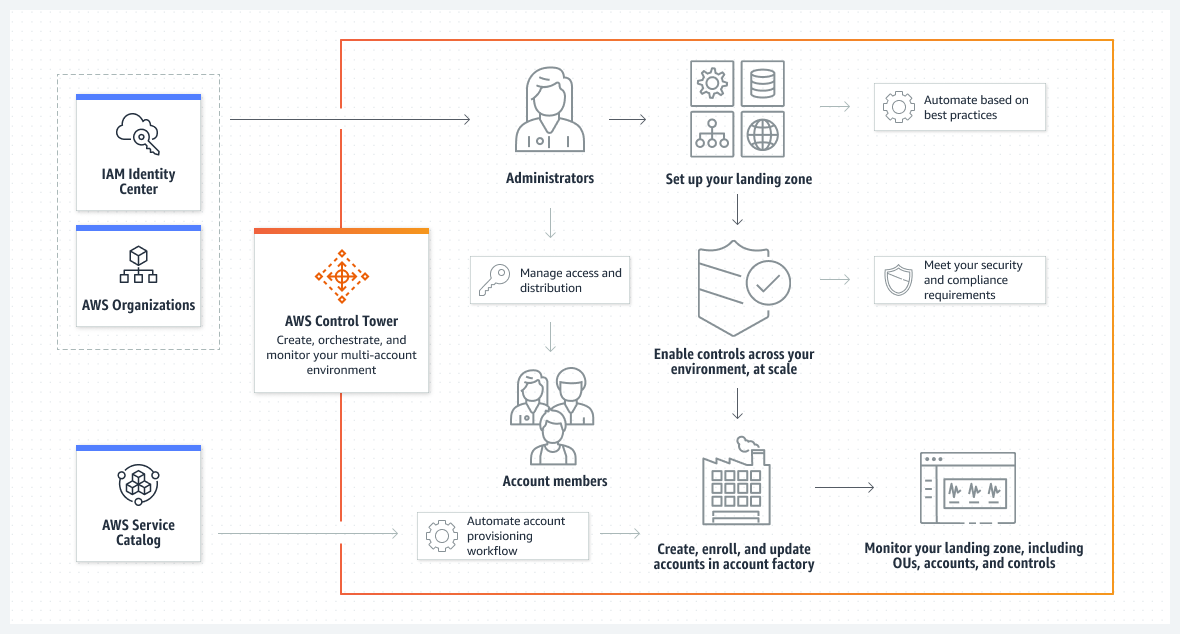
- AWS Control Tower - AWS Control Tower provides a way to create and manage a multi-account environment that follows AWS best practices. AWS Control Tower does not create the resources necessary to deploy an application.
- AWS Auto Scaling - AWS Auto Scaling monitors applications or workloads that run on AWS and automatically adjusts the resource capacity to meet demand. AWS Auto
- AWS System Manager Session Manager - Session Manager is a node management service for the cloud or for on-premises compute units. Session Manager provides a secure connection through shell scripting. You can establish the connection without the need to open ports.
- AWS Config - WS Config is a fully managed service that can provide inventory and configuration history audit reports of AWS resources.
- AWS Artifact - AWS Artifact provides a central location to access AWS security and compliance reports and agreements. AWS Artifact DOES NOT audit or document changes to AWS resources. Allow customers to manage their agreements with AWS.
- Amazon Health Dashboard - Health Dashboard gives you the ability to see the status and health of all AWS services. The dashboard also shows reported service-related events for services across AWS Regions. Detailed troubleshooting guides.
- AWS Compute Optimizer - Compute Optimizer helps avoid overprovisioning and underprovisioning four types of AWS resources—Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance types, Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes, Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) services on AWS Fargate, and AWS Lambda functions—based on your utilization data. **Rightsizing!
- AWS Resource Groups and Tag Editor - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/resource-groups-and-tagging/ - Quickly identify resources that belong to a specific project, Track AWS spending across multiple resources.
- AWS Service Catalog - AWS Service Catalog lets you centrally manage your cloud resources to achieve governance at scale of your infrastructure as code (IaC) templates, written in CloudFormation or Terraform configurations. With AWS Service Catalog, you can meet your compliance requirements while making sure your customers can quickly deploy the cloud resources they need.It simplifies organizing and governing commonly deployed IT services.
- AWS Launch Wizard - AWS Launch Wizard offers a guided way of sizing, configuring, and deploying AWS resources for third party applications, such as Microsoft SQL Server Always On and HANA based SAP systems, without the need to manually identify and provision individual AWS resources. To start, you input your application requirements, including performance, number of nodes, and connectivity on the service console. Launch Wizard then identifies the right AWS resources, such as EC2 instances and EBS volumes, to deploy and run your application. Launch Wizard provides an estimated cost of deployment, and lets you modify your resources to instantly view an updated cost assessment. Once you approve the AWS resources, Launch Wizard automatically provisions and configures the selected resources to create a fully-functioning, production-ready application. Also creates CloudFormation templates.
- AWS OpsWorks - - OpsWorks is a configuration management service that uses Chef and Puppet, automation platforms that allow you to use code to automate the configurations of your servers. It lets you model and manage your application and its entire lifecycle from physical servers, virtual machines, to containers, and even serverless architectures. It provides a simple and flexible way to manage application stacks and supports a wide range of application architectures and deployment workflows.
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) - AWS Certificate Manager is a service that lets you easily provision, manage, and deploy Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) certificates for use with AWS services and your internal connected resources.
- AWS Well-Architected Tool - The AWS Well-Architected Tool helps you review the state of your workloads and compares them to the latest AWS architectural best practices.
- AWS License Manager - AWS License Manager makes it easier for you to manage your software licenses from vendors, such as Microsoft, SAP, Oracle, and IBM, across AWS and your on-premises environments.
- AWS Systems Manager - AWS Systems Manager is a secure end-to-end management solution for resources on AWS and in multicloud and hybrid environments.
- AWS Audit Manager-AWS Audit Manager to map your compliance requirements to AWS usage data with prebuilt and custom frameworks and automated evidence collection.
Machine Learning
- Amazon Rekognition - Amazon Rekognition uses pre-trained machine learning models to detect objects in images.
- Amazon Lex - Design, Build, Test, and Deploy Conversational Interfaces (ChatBots) with Alexa.
- Amazon Kendra - Amazon Kendra is an intelligent (machine learning) enterprise search service,
- Amazon Comprehend - Amazon Comprehend is a Natural Language Processing service that uses machine learning to uncover valuable insights and connections in text.
Cloud Financial Management
- AWS Budgets - In AWS Budgets, you can create budgets to plan your service usage, service costs, and instance reservations. The information is updated three times a day.
- AWS Marketplace - Provides
- Protects customers by performing periodic security checks on listed products.
- Provides flexible pricing options that suit most customer needs.
Application Integration
- Amazon EventBridge - Amazon EventBridge Event Bus is a serverless event bus that helps you receive, filter, transform, route, and deliver events
- AWS Step Function - AWS Step Functions is a visual workflow service that helps developers use AWS services to build distributed applications, automate processes, orchestrate microservices, and create data and machine learning (ML) pipelines. **serverless orchestration
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) - Send/store/receive message (payload) between software components at any volume , where messages are placed before they are processed
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) - used to send messages to services, but also notification to end users (use Pub-Sub model, called SNS topic. users sub to topic, and topic publishes to subs. **
Business Application
- Amazon Connect - Set up a scalable contact center in AWS Cloud. Not used to encrypt traffic between two different networks.
Frontend Web and Mobile
- AWS Device Farm - Device Farm is a mobile application testing service. You can use Device Farm to perform automated testing with Android, iOS, and web applications on real, physical phones and tablets that are hosted by AWS.
- AWS Amplify - Amplify helps you build full stack web applications and mobile.
- AWS AppSync - AppSync creates serverless GraphQL and Pub/Sub APIs that simplify application development through a single endpoint to securely query, update, or publish data.
End User Computing
- Amazon AppStream 2.0 - AppStream 2.0 is an application streaming service. AppStream 2.0 provides instant access to your desktop applications from anywhere. AppStream 2.0 does not provide access to virtual desktop infrastructure → more focused on individual applications compared to workspace
- Amazon Workspaces - WorkSpaces can run a cloud desktop directly on many kinds of devices. WorkSpaces can run on PC, Mac, iPad, or Kindle Fire. Therefore, users can securely interact with company-provided desktops through their personal devices.
- Amazon Workspaces Web -
Containers
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) - ECR is a fully managed Docker container registry that makes it easy to store, share, and deploy container images
Developer Tools
- AWS AppConfig: This service allows you to create, manage, and quickly deploy application configurations. AppConfig can be used to manage features, enable A/B testing, and roll out configuration changes safely without affecting the application’s availability.
- AWS CLI (Command Line Interface): AWS CLI is a unified tool to manage your AWS services. With just one tool, you can control multiple AWS services from the command line and automate them through scripts.
- AWS Cloud9: Cloud9 is a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) that lets you write, run, and debug your code with just a browser. It includes a code editor, debugger, and terminal. Cloud9 comes prepackaged with essential tools for popular programming languages.
- AWS CloudShell: CloudShell is a browser-based shell that provides command-line access to AWS resources directly from the AWS Management Console. It pre-installs the AWS CLI and other useful command-line tools, making it easier to manage AWS resources.
- AWS CodeArtifact: CodeArtifact is a fully managed artifact repository service that makes it easy for organizations to securely store, publish, and share software packages used in their software development process.
- AWS CodeBuild: CodeBuild is a fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces software packages that are ready to deploy. It eliminates the need to provision, manage, and scale your own build servers.
- AWS CodeCommit: CodeCommit is a fully managed source control service that hosts secure Git-based repositories. It makes it easy for teams to collaborate on code in a secure and highly scalable ecosystem.
- AWS CodeDeploy: CodeDeploy automates code deployments to any instance, including Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers. It makes it easier to rapidly release new features, helps avoid downtime during application deployment, and handles the complexity of updating applications.
- AWS CodePipeline: CodePipeline is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service for fast and reliable application and infrastructure updates. It builds, tests, and deploys your code every time there is a code change, based on the release process models you define.
- AWS CodeStar: CodeStar enables you to quickly develop, build, and deploy applications on AWS. It provides a unified user interface, allowing you to easily manage your software development activities in one place.
- AWS X-Ray: X-Ray helps developers analyze and debug production, distributed applications, such as those built using a microservices architecture. With X-Ray, you can understand how your application and its underlying services are performing to identify and troubleshoot the root cause of performance issues and errors.
Migration and Transfer
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) - AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) is a managed migration and replication service that helps move your database and analytics workloads to AWS quickly, securely, and with minimal downtime and zero data loss.
- AWS Application Migration Service (AMS) - AWS Application Migration Service, formerly known as CloudEndure Migration, is designed to simplify and accelerate the process of migrating applications to AWS.
- AWS Transfer Family - AWS Transfer Family securely scales your recurring business-to-business file transfers to AWS Storage services using SFTP, FTPS, FTP, and AS2 protocols.
- AWS Schema Conversion Tools (AWS SCT) - AWS Schema Conversation Tools offers two schema conversion solutions to make heterogeneous database migrations predictable, fast, secure, and simple.
- AWS Migration Hub - AWS Migration Hub provides a central location to monitor and manage migrations to AWS. It simplifies the process of migrating servers, databases, applications, and entire workloads to AWS by offering a unified interface that aggregates migration information from various AWS and partner migration tools. This enables organizations to plan, track, and complete migrations from a single console, making the process more streamlined and manageable.
-
- AWS Application Discovery Service - AWS Application Discovery Service helps you plan your migration to the AWS cloud by collecting usage and configuration data about your on-premises servers and databases. Application Discovery Service is integrated with AWS Migration Hub
- AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) - SMS is an agentless service which makes it easier and faster for you to migrate thousands of on-premises workloads to AWS. AWS SMS allows you to automate, schedule, and track incremental replications of live server volumes, making it easier for you to coordinate large-scale server migrations.
Internet of Things
- AWS IoT Core - AWS IoT Core is a managed cloud service that lets connected devices easily and securely interact with cloud applications and other devices.
- AWS IoT Greengrass - AWS IoT Greengrass is software that extends cloud capabilities to local devices, enabling them to collect and analyze data closer to the source of information, while still using the cloud for management, analytics, and durable storage. Greengrass devices can run AWS Lambda functions, Docker containers, or both, execute predictions based on machine learning models, keep device data in sync, and communicate with other devices securely – even when not connected to the Internet.
Customer Engagement
- AWS Activate for Startups - AWS Activate provides resources to help startups build and grow on AWS.
- AWS IQ - Complete projects faster with help from third-party AWS Certified experts
- AWS Managed Services (AMS) - IT operations management for AWS
- AWS Support - Contact AWS for technical and account support.
Other
- AWS Ground Station
- AWS Elastic Load Balancing - Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) helps properly distribute traffic in high performance, cost-efficient, highly available, automatically scalable that you can set and forget. Is a regional construct (can redirect traffic to multiple AZ’s). ELB is automatically scalable (ELB scales for more throughput with no additional cost). Performs health checks.
- When new instances come online, they communicate with ELB and ELB scales up and starts rerouting traffic.
- When services scale down, ELB stops traffic to those instances that are terminated and EC2 automatically terminates those instances after existing requests are all handled.
05 Support Plans
Support plans are… In-depth can be found here https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/plans/.
- Basic
- Developer
- Business
- Enterprise on-ramp
- Enterprise
| 24/7 | TAC | B | SB | TAM | IEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | web during business | 7 | y | y | ||
| Developer | yes | 7 | y | y | ||
| Business | yes | all | y | y | ||
| Enterprise | yes | all | y | y | y | y |
- B - Bulliten
- SB - Security Board
- TAM - Technical Account Managmer
- IEM - Infrastructure Event Management
- TAC - Technical Advisor Checks (Core checks)
Services
- AWS Support Concierge
- AWS Customer Service
- AWS Operations Support
- AWS Abuse Team
- AWS Professional Services
06 Job Roles in the Cloud
On Premisis
- IT Solutions Architect - creates the high level solutions for business applications, systems, portfolios, infrastrctures, or an entire enterpise. They develop IT services and solutions for companies and organizations and often design and manage communications, security, networking, and storage.
- System Administrator - keeps servers operations. They ensure servers meet uptime goals. They are responsible for patching or upgrading operating systems, hardware, an hypervisors. They make sure system backups occur.
- responsible for the overal performance of the cloud, keep systems working together by managing configurations, completing detailed tasks, and assisting administrators with setting up databases servers
- Network Administrator
- Desktop Administrator
- Applications Administrator
- Database Administrator
In CLoud
- Cloud Architect - responsible for delivering an overall cloud strategy and is in charge of the entire cloud environment.
- System Administrator - responsible for overall performance of cloud systems,
- must be proficient with configuration and management changes
- Security Administrator - responsible for the overall integrity, confidentiality, and protection of data and resources in the cloud.
- DevOps Administrator - responsible for managing developers and orchestrating the numerous tools and stages in the pipeline.
- must be proficient with scripting languages
- Systems Operations
Mapping after Transition
- IT Solutions Architect - > Cloud Architect
- System Administrator → System Administrator
- Network, Desktop → System Operations and Security Administrator
- Application, Database → DevOps Administrator
07 Challenging Topics
EBS
- 16 TiB
- survive termination of EC2 instance
- solid state by default
- HDD options
- better for complex read/write function S3
- unlimited
- 5000 GB of objects
- write once/read many
- 99.999999999% durability
- web enabled
- regionally distributed,
- 11 9’s of durability
- cost savings
- serverless
Object vs Block Storage
- object treats each file as a complete, discrete file → good for documents, images, video files, but not good for breaking apart files (such as long videos) and micro edits. S3 for example, using object storage would have to reupload the entire file.
EFS vs EBS
- What is the differences between EBS?
- EBS attach to EC2, availability zone level resource, need to be in the same availability zone to attach EC2 instances
- EBS volumes do not automatically scale
- block storage
Security Group vs Network Access Control List
- Security group is the firewall of EC2 Instances.
- Network ACL is the firewall of the VPC Subnets.
AWS DMS vs AWS Snow Family?
Amazon Health Dashboard vs Amazon Inspector vs AWS Trusted Advisor
- AWS Service Health Dashboard focuses on the health and availability of AWS services globally.
- Amazon Inspector focuses on the security assessment of AWS resources, identifying vulnerabilities and offering recommendations for mitigation.
- AWS Trusted Advisor provides broad recommendations across cost optimization, security, performance, and fault tolerance to ensure best practices are being followed in the AWS environment. Categories include
- fault tolerance
- performance
- resilience
- security
- operational excellence,
- service limits,
- recommend actions
Data Migration Service vs Snow Family vs Transfer Family
- DMS is best suited for live database migrations with minimal downtime, supporting a wide range of database sources and targets, and capable of handling ongoing data replication needs.
- Snowball is optimized for transferring very large datasets into or out of AWS, bypassing the limitations of internet bandwidth and providing a physical, secure method for large-scale data migration.
Amazon Detective vs Amazon Macie
Amazon Security Hub, AWS Firewall manager, AWS Network Firewall, AWS Shield and AWS WAF
AWS Control Tower vs AWS IAM
AWS Local Zones vs AWS Outposts vs AWS Edge Locations
AWS Athena vs Amazon EMR vs Amazon QuickSight
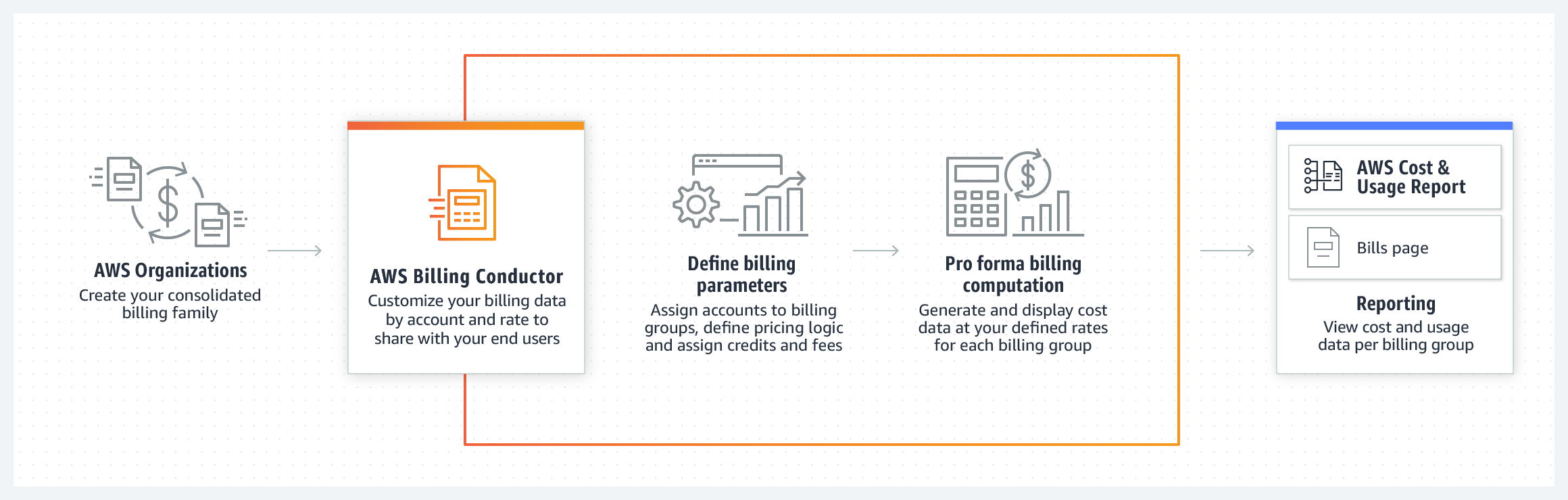
AWS Orgaanization vs AWS Billing Conductor vs etc
Application Migration Hub vs Application Discovery Service
SaaS, IaaS, PaaS
AWS Cost Explorer vs AWS Budgets vs AWS Cost and Usage report vs WS Billing dashboard
- Cost Explorer - can forecast future AWS costs.
- Cost and Usage Report - can view the most granular data about your AWS bill