Software Development
Table of Contents
00 Background
Resources
Books
- 📖 (2021) The DevOps Handbook Second Edition
- 📖 (2018) The Phoenix Project
- 📖 (2018) Accelerate: Building and Scaling High Performing Technology Organizations
- 📖 (2016) Effective DevOps
- 📖 (2016) The DevOps Handbook First Edition
- 📖 (2016) Site Reliability Engineering
- 📖 (2015) DevOps in Practice
- 📖 (2010) Continuous Delivery
- 📹 DevOps Engineering Course for Beginners https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j5Zsa_eOXeY ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
Certifications
- Cloud Certified
- SysOps Administrator
Documentations
02 Technologies
Current Core Technologies Here is a summary of common core technologies…
- Development: Git/Github/Gitlab
- Build:
- Testing: Github Actions, Bitrise, LayerCI, CircleCI
- Code Coverage: Codecov, COVERALLS, CODE CLIMATE, Cyprus
- Deploy: Docker, Google Cloud, AWS Cloud
- Monitor:
- Logging Aggregation - ELK(Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana), DataDog
- Metrics Monitoring - Prometheus, Grafana,
- Operate: Kubernetes, Ansible (Configuration management), Jenkins (CI and CD)
Frameworks
03 Practices
Agile Software Development
- user stories
- epics (work that can be broken down into specific tasks)
by using an agile approach with epics, you start small, iterate, measure, manage, and scale. With this approach, you do the following.
- Structure your work in the form of epics and stories to be able to respond to change
- produce a well-prioritized backlog
- report your progress
todo The importance of
SCRUM
Lean
01 DevOps
Here, we understand the general development cycle of an application.
What is DevOps? A methodology that helps engineering teams build better products by continuously integrating user feedback.
DevOps Engineering is vital for engineering teams as product matures.
What is DevOps Engineering? Practical use of DevOps within software engineering teams. Being able to build, test, release and monitor.
Here are the pillers of DevOps engineering.
- pull request automation
- deployment automation
- application performance management
Pull Request Automation
- Developers share code changes using version control systems.
- A set of code changes is called a “pull request” and “merge request”
- If pull requests are approved (through code review, feedback from product manager, engineering manager, designers, marketers, C-suite), the code changes can go into the main codebase Deployment Automation
- Deploy a feature to a certain set of users as final test before rolling it out publically
- Start new versions of services without casing downtine
- rolling back to the prior version in case something does go wrong
- Spinnker, harness Application Performance Management
- Metrics - numeric measurements of key numbers in production
- Logging - text descriptions of what is happening during processing
- Monitoring - take metrics and logs to convert them into health metrics
- Alerting - If monitoring detects a problem, it notifies developer
What can you automate?
- continuous integration (CI)
- per change ephemeral environments
- automated security scanning
- notifications to reviewers
Common Sections Dev
- Plan - Agile practices/development - SCRUM, Sprint, Lean
- Code - Developers and pushing code to version control
- Build -
- Test - automatic (continuous integration) and manual (quality assurance) Ops
- Release - automatic
- Deploy - (release + deploy = continual deployment)
- Operate - scaling, architectural problems
- Monitor -
Development (Dev)
Plan
Reference Agile Software Development
Code
Version control…
Build
Test
Test Driven Development Definition (TDD)
- TDD - tests are written before code is written
- Unit Tests - ensure individual components work on their own
- Integration Tests - ensure components work together
- System (end to end tests) - ensure everything works together
- Acceptance Tests - can users accept it
Workflow iwthout TDD? (1) choose something to work on (2) build it based on specifications (3) test it with small scripts
With (1) choose something to work on (2) write tests that would pass if product works (3) keep building until all tests pass
TDD forces you to priortize tasks to ensure no major issues are seen by customers.
Should have a test priority!
- High value features
- Edge cases in high value features
- Things that are easy to break
- Basic React component testing
Operations (Ops)
Release and Deploy (Continuous Deployment)
Deployment Strategies
Deploying - virtual machines (VMs) and Containers - to linux
The big change for moving programs into containers or VMs is that each will have its own versions of shared resourecs like files and network ports
With
- resource sharing
- environments (different versions of files)
- conflicting gwebsevers listening to the same port
sandbox or isolated
Rolling Deployments Strategy to deploy a new version of an application without causing douwntime. They work by creating a single intance of the new version of an application, then shutting off one instance of the old version until all intances have been upgrade.
Benefits
- well supported
- no huge bursts
- easily reverted
Cons
- Speed
- API Compatability
Blue/Green Deployment Starting an entirely new instance of an application and then routing traffic over to it.
Benefits
- Easy to understand, powerful, extendable to workflows COns: Difficult to make hotfixes, resources allocation is not convenient, clusters can affect each other
Rainbow Deployments
Acceptance Test New version of the app could be tested against the production database in the very environment which will soon become production. Tested by QA
Canary Deployments
Operate and Monitor
Devops is an end goal for an organization!
For example, a new startup with no users building a web application doesn’t necessarily need deployment automation and application performance management, instead a simple stack of GitHub, Netfily/Vercel, and LayerCI would suffice. On another hand, a team building an application for 10 enterprise users, who are more sensitive sensitive to downtime, and require test coverage and business hours alerting should be priorities. Example stack includes GitHub, Sentry, PagerDuty, CodeCov, Bitrise
Continuous iNtegration Definition Developers pushing many small changes to a repository. These changes are verified by an automatic software that runs comprehensive tests to ensure.
CI is the first step to DevOps automation and helps with code collaboration. CI helps improve developer speed because new changes can be made without breaking existing code. CI helps reduce customer churn and user satisfaction by preventing broken code from publishing.
CI is a vital tool for developer collaboration, Increase collaboration, prevent errors, and increase user satisfication.
Branch Based Github..
Code Coverage Definition Methodology that quantitively measures how comprehensive a code base’s test are. Increasing code cpverage often increases stability and reduces bugs.
When to care about code coverage?
- your product has users and those users might leave if they are affected by bugs
- you are working with developers that aren’t immediately trustworthy like contractors/interns
- you are working on a very large code base with many testabale components
Common mistake - too many test for uncertain features
Don’t over optimize for features that don’t matter
Rule 1 - code coverage must not decrease (but may have exceptions for certain pieces of code) Rule 2 - code owners for test files themselves, developers can change implementation details without review, but logic changes (changing tests) would require senior developers.
If you are working in a large code base using TDD, hiring interns/contractors or have usrs sensitvive to bugs, it’s time to measure code coverage.
Linting Approximates testing, but doesn’t require any additional time. Linters look at a program’s source code and find problems automatically. They are common features of pull request automation because they ensure that “obvious” bugs do not make it to production.
Example.
var x = "5"
function f(elements) {console.log(elements)}
let x = 0;
while(x<100) {
console.log(x);
}There is a couple errors. Rules like “don’t shadow variables” Don’t waste time on style code review, “tabs or spaces”, camelCase or pothole_case?
https://google.github.io/styleguide/
The Nit Approach Definition Code reviewers leave little comments on the code called “nits” that the team can icgnore until broader reviews. Nits are helpful as future references to prevent blocking important changes.
Autoformattors Tools that help apply code style rules based on the style guide your team has chosen automatically.
Example.
npm run lint
Good solution in CI: automatically fix the issues
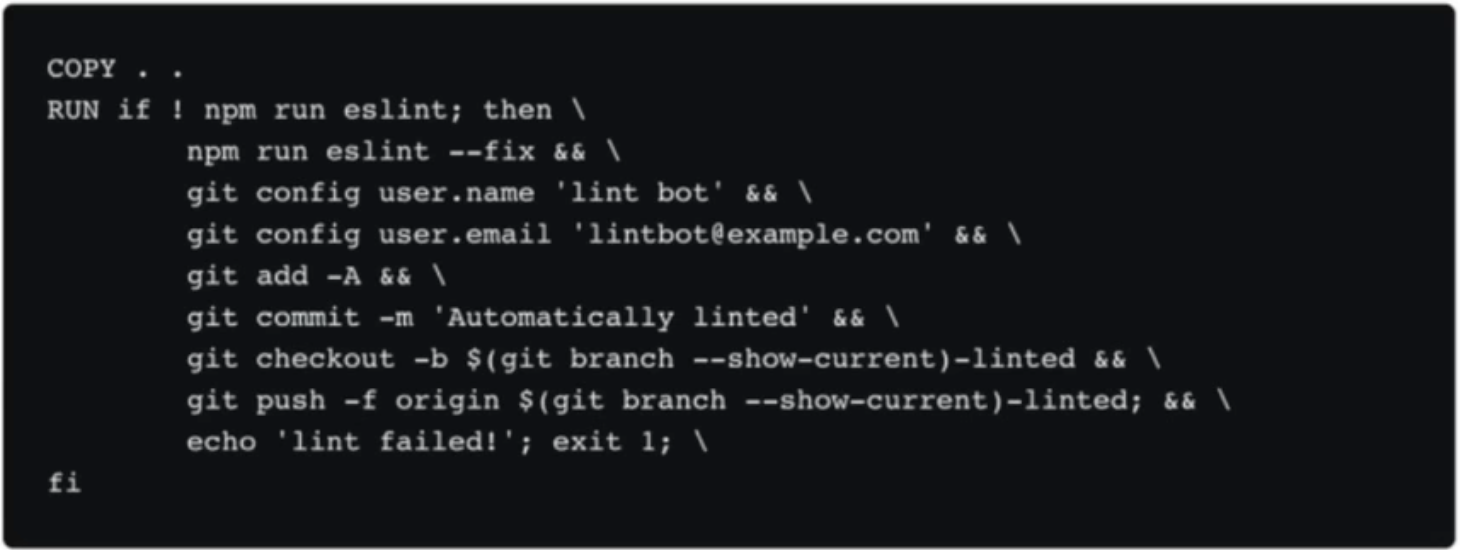
Examples of Linters
![note] Any team with more than one developer working in the same codebase should setup a linter to catch obvious bugs
Ephemeral Environments Temporary deployments that have self-contaiend version of your application, generally every feature branch.
Halfway between development and staging environment. Extreme case continuous staging.
Benefits
- Accelerates software development lifecycle
- Allows developers to share changes with designers, managers, and other stakeholders.
Debounce?
Difficulties
- Database migration
- Lifecycle management
- tie the lifecycle to the life of a pull request or merge request → expensive
- create a ChatOps bot that allows creating a new environment for a specific branch with a small tiime → slow, don’t know life
- create an ephemeral environment for every commit, and hibernate them the second they are provisined, then wake them up as they are required.
CI/CD is merged with ephermeral environments to form a unified CI/CD and review process for every commit.
AutoScaling
Automates horizontal scaling to ensure that the number of workers (enough resources) is porportional to the load on the system
Service Discovery A key problem in deployment is getting services to be able to find each other (database vs server vs frontend).
Service discovery becomes important when
- you want “zero downtime deploymeents”
- you have more than a couple of micro severs
- you are deploying to several enviroments
Methods
- Static and manual
- Store the service IPs in a hash table
- Reverse proxy with proxy pass
- Service discover via DNS (globally or locally), map hostnames to IPs.
By decopling application logic from deployment logic, you will help faster production
Application Performance Management
Log Aggregation It’s a way of collecting and tagging application logs from many different services into a single dashboard that can easily be searched.
Adding authentication to your logging frontend via Nginix
auth_request
Vital Production Metrics
- CPU, Memory, Disk I/O
Quartile Analysis