Data Science
TODO Reorganize this notes This note focuses on data science. Although Machine learning and Deep learning are now aspects of Data Science, this note focus more on data data engineering, data science, data analysis, and more traditional data science aspects.
00 Temp
reproducible research, vs replication?
- analytic data are available
- analytic code are available
- documentation of code and data
- standard means of distribution
01 Background
What is Data Science and what is the role of a Data Scientist? An Economist Special Report sums up this melange of skills well - they state that a data scientist is broadly defined as someone:
“who combines the skills of software programmer, statistician and storyteller slash artist to extract the nuggets of gold hidden under mountains of data”
- Intro to Data Science - Crash Course for Beginners
- Learn Data Science Tutorial — Full Course for Beginners
What are some good Platforms to practice Data Science?
- Platforms: (1) Kaggle
- Datasets: (1) Human Development Reports https://hdr.undp.org
What are some core Data Science Technologies?
Resources
Key 🟢 Completed 🟡 Working On 🔴 Not Yet Started
📹 Lectures 📖 Books 🌐 Online PDFs, Articles
- 📹 IBM Data Science Professional Certificate by Coursera 🟢
- 📹 IBM Data Analytics Professional Certificate by Coursera 🟢
- 📹 Meta Backend Development by Coursera 🟢
- 📹 Introduction to TensorFlow for Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning by Coursera 🟢
- 📹 IBM AI Engineering Professional Certificate by Courser 🔴
- 📹 IBM Applied AI Professional Certificate by Coursera 🔴
- 📹 IBM Data Engineering by Coursera 🔴
- 📹 Deep Learning Specialization 🟢
- 📹 Generative AI with Large Language Models 🔴
- 📹 Machine Learning Specialization, DeeplearningAI with Andrew NG on Youtube 🔴
- 📖 Machine Learning with Pytorch and Scikit 🟡
- 📖 Introduction to Mathematical Statistics 🟡
- 🌐 Deep Learning by Purdue Spring 2024
- 📹 (2023) MIT 6.S191: Introduction to Deep Learning on Youtube
- 📹 (2018) Stanford CS229: Machine Learning Course on Youtube
Books Beautiful Evidence…
02 Math
What is the importance of math in data analytics, data science, and deep learning? Statistics Resources
- 📖 Introduction to Mathematical Statistics
- Topics skipped: Transformations, Moment Generating Functions, Multivariate Normal Distribution, t- and F-Distributions, Mixture Distributions,
- 📖 The Elements of Statistical Learning
- 📖 Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective
03 (Big) Data and Database
What is the importance of database and data in data science? Database
**Types of Databases
- RDBMS - rigid definition using structured, ACID compliance,
- NoSQL - ability to handle large volumes of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data
- Key-Value Store
- Pros: Great storing user session data, user pro
- Cons: Not a great fit if you want to query data on specific data values. Need relationships between data values. Need multiple unique keys
- Document-Based - store each record and its associated data within a single document
- Cons: Not great to run complex queries. Perform multi-operation transactions.
- Column-based - Data is stored in cells grouped as columns of data instead of rows
- Cons: Not good for complex queries
- Graph Based
- Profs: Good for
- Cons: Not good for processing high volumes of transactions
- Key-Value Store
Characteristics of Big Data
Era of Big Data qualitative vs quantitive, three v’s of data (volume, velocity, variety)
data types
- structured
- unstructured
What is Data Mining? The process of extracting knowledge from data. An interdisciplinary field that involves the use of pattern recognition technologies, statistical analysis, and mathematical techniques Aims to identify correlations in data, find patterns and variations, understand trends, and predict probabilities.
**What are data repositories?
- Databases
- Data Warehouses
- Data Marts
- Data Lakes
- Big Data Stores
**Common sources of data
- relational databse
- flat files and xml datasets
- apis and web services
- web scraping
- data streams and feeds
04 Important Concepts and Questions
- Data Science Reports, Literate Statistical Programming
- Types of Data Analysis
- Descriptive Statistics
- Explanatory Statistics: Mean Squared Error, Coefficient of Determinism, Pearson Coefficient, F1 Score, Precision, Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity
- Inferential
- Predictive
- Mechanistic
- Causal
- Data Visualization
- Core Concepts - Show comparisons, show casuality, mechanism, explanation, sysmetic structure, show multivariate data, integration of evidence
- Plots - Residual Plots, Distribution Plots, Line Plots, Waffle Charts, Area Plots, Histogram, Scatter Plots Box Plot, Bar Charts, Pie Charts, Heatmaps, Area Plots, Geospatial Maps (Forium) w/ GeoJson File, Count Plot, Bubble Plot, PairPlot, Scatter Plot fit Lines with Confidence Intervals
- Tools: Python, R, Tabeau, Power BI, Microsoft Excel
- Machine Learning
- Tasks: Linear Regression, Classification, Clustering, Association, Anomaly Detection, Sequence Mining, Dimension Reduction, Recommendation Systems
- Algorithms: Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines, K-Means, K-Modes K-Nearest Neighbor, Random Forest, XGBoost, Naive Bayes
- Types of Learning: Supervised, Unsupervised, Self-Supervised, Transfer Learning, Reinforcement Learning
- Fields/Applications:
- Computer Vision: (1) Image classification (2) Object Detection (3) Semantic Segmentation (4) Image Segmentation (5) Video Classification
- Natural Language Processing: (1) Machine Translation (2) Semantic Analysis (3) Named Entity Recognition
- Automated Speech Recognition: (1) Trigger Word Detection
- Time Series
- Recommendation Systems
- Core Concepts: Bias/Variance, Normalization, Train/Dev/Test Sets
- Exhaustive Grid Search - model tuning for variables like c in Support Vector Machines, K-Nearest Neighbor, and Number of layers in Neural Networks
- TODO: Analyze U-Net,
- Neural Networks
- Architectures: Convolutional Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network (GRU, Simple RNN, Sequence to Vector RNN, Sequence to Sequence RNN, LSTMs), Transformers, Generative Adversarial Networks,
- Core Concepts: Input/Output Shape, Loss Functions, Optimizers, Activation Functions, Mini-batch Gradient Descent, Convergence, Callbacks/Early Stopping, Data Augmentation, Dropout, Vanishing/Exploding Gradients,
- Excel, Pivot tables, VLookup, HLookup,
Data Engineer vs Data Analyst vs Data Scientist vs Business Intelligence
The roles of Data Analyst and Data Scientists are extremely similar.
Let’s see how IBM differentiates the two through their IBM Data Science Professional Certificate Course and IBM Data Analytics Professional Course.
Data Analysts can develop into Data Engineers, Data Scientists, Business Analysts, or Busines Intelligence Analysts
I believe Data Engineer and Business Analyst .
Summary
- Data Engineering convert raw data into usable data
- Data Analytics use this data to generate insights
- Data Scientists use Data Analytics and Data Engineering to predict the future using data from the past
- Business Analysts and Business Intelligence Analyst to use these insights and predictions to drive decisions that benefit and grow their business
Data Analysts Responsibilities
- Gather, clean, analyze, and mine data
- Interpret results
- Report findings
 What is the difference between descriptive and explanatory statistics?
What is the difference between descriptive and explanatory statistics?
What is out-of-sample vs in-sample? For example, in-sample training accuracy is the percentage of correct predictions that the model makes when using the test dataset for training. But a high-training accuracy isn’t necessarily a good thing, easily causing over-fit.
Out-of-sample accuracy!
Predictive vs Descriptive Models?
Predictive models find causality, relationships between explanatory variables and dependent variables.
- A predictive model tries to yield yes/no or stop/go outcomes Descriptive models find clusters of data elements with similar characteristics
- Might examine, if a person did this, then they’re like to prefer that
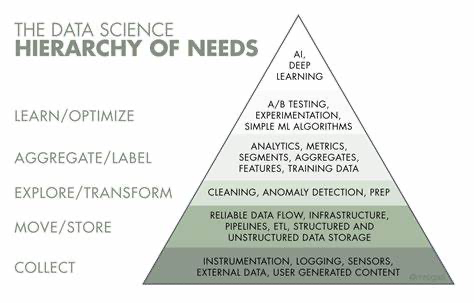
Full Stack Architecture of AI
[
06 Interview Preparation
What are the most important qualities of a Data Analyst?
- curiosity
- detailed-oriented
- love technology
- love numbers and information
- presentation skills
- integrity and detailed oriented
- clear communication
- ability to understand complex analysis
- AB tests
- SQL
- Flexible - be able to pick up technical quickly
- Dynamic and Adaptable
Different types of Data Analysis
- Descriptive Analytics - “what happened”, insights about past events
- Diagnostic Analytics - “why did it happen”, insights from descriptive analytics to dig deeper to find cause of outcome
- Predictive Analytics - “what will happen” → not what will, instead what might, meaning probabilistic
- Prescriptive Analytics - “what should be done about it”
Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Descriptive Statistics - summarizing information about the sample
- Central Tendency - mean, median, mode
- Dispersion - variance, standard deviation, range
- Skewness - distribution of values is symmetrical around a central value or not Inferential Statistics - making inferences or generalizations about the broader population from which a sample was drawn (use a relatively small sample of data to say something about the population at large)
- hypothesis testing
- confidence intervals
- logistic regression
Steps of Data Analysis Process coursera - ibm - data analysis
- understanding the problem and desired result
- setting a clear metric
- gathering data
- cleaning data
- analyze and mining data
- interpreting results
- presenting the data
coursera - john hopkins - r foundations
- forming the question
- finding or generating the dat
- data are then analyzed
- exploring the data
- modeling the data
- communicate to others
**What is Data Wrangling
- Discovery
- Transformation →
- Structuring (joins and unions)
- Normalizing 0 clean the data base of unused and redundant data
- Denormalizing - combine data from multiple tables into a single table so that it can be queried faster
- Cleaning: Inaccuracies, Missing Data, Incomplete Data, Biases in Data, Null Values, Outliers
- Inspection
- Clearning
- Verification
- Enriching: Adding data points that make the analysis more meaningful.
- Validation
- Publishing - delivering the output of the wrangled data for downstream
- Documentation
Tools for Data Wrangling
- Excel Power Query / Spreadsheets
- OpenRefine
- Google Data Prep
- Watson Studio Refinery
- Trifacta Wrangler
- Python and R
IBM SPSS Statistics Stands for Statistical Process for Social Sciences
- popularly used for advanced analytics, text analytics, trend analysis, validation of assumptions, and translation of business problems into data science solutions